On 21st May 2024, 43 senior finance practitioners from Philip Morris, Markem-Imaje, COFCO International, MSC Cruises, JTI, Hôpital de la Tour, Cargill, Richemont, Unilabs, PepsiCo, and many other companies gathered to discuss the transformative potential of the FP&A Trends Maturity Model and how to create your transformation map with this tool. This time, the meeting was hosted in the beautiful Quartier des Banques in the centre of Geneva.
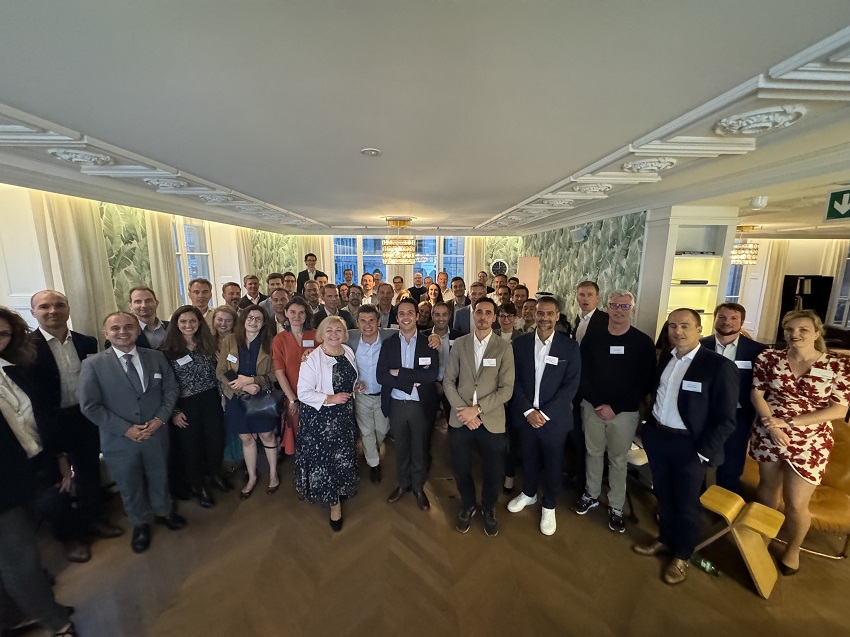

Figure 1: Geneva FP&A Board №16 Participants, May 2024
This discussion was sponsored by Wolters Kluwer/CCH Tagetik® in partnership with IWG, Michael Page and Page Executive.
What Holds Us Back from Analytical Transformation?
As usual, the meeting was led by Larysa Melnychuk, Managing Director of the International FP&A Board, who guided the discussion on this analytical and visionary subject.
At the beginning of the meeting, each participant was asked to share their views on the main obstacle to FP&A Transformation. The most repetitive feedback was on data quality and structure, competing priorities, and organisational culture. Other reasons, such as mindset and resources, were also frequently mentioned. This largely coincided with the unified insights from eight other FP&A Board chapters, where most insights were centred around data, time, people, insights, and mindset.
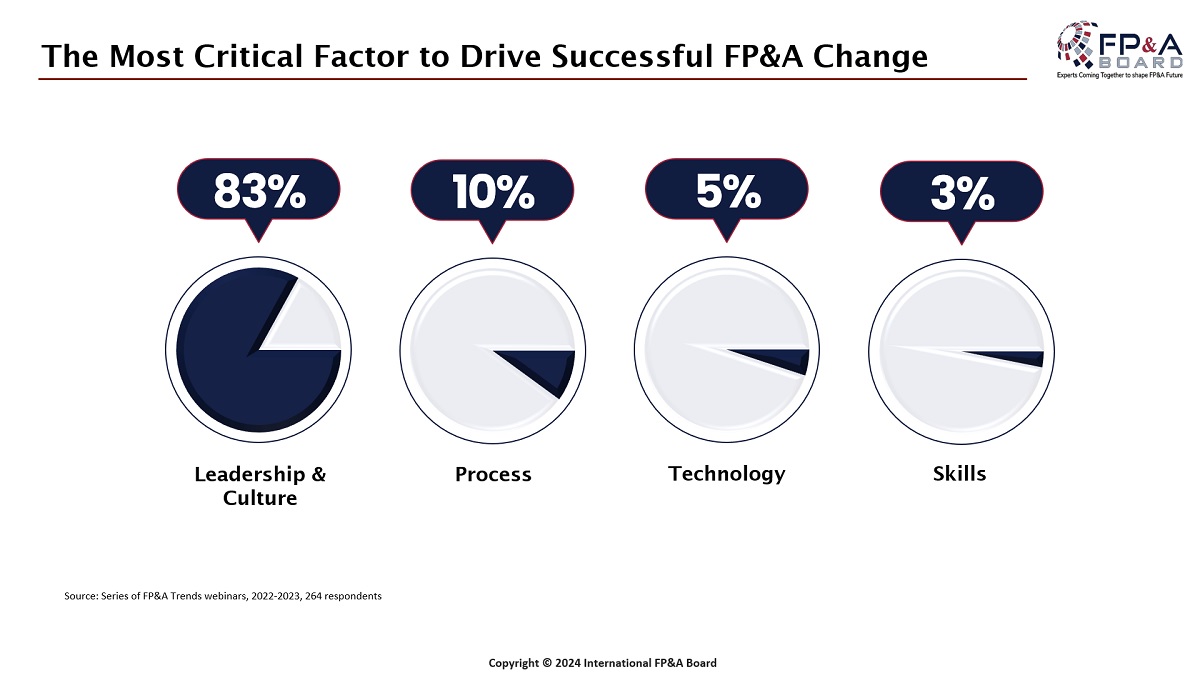
Figure 2
Larysa Melnychuk then shared the results from a series of FP&A Trends webinars held between 2020 and 2023, where 83% of the respondents named leadership and culture the most critical factors for a successful FP&A change. The presentation of the FP&A Trends Maturity Model followed with its four steps:
- WHY – General overview of the model
- WHAT – Six dimensions and Five stages of FP&A Maturity
- HOW – Steps for moving to the Leading State
- HOW Exactly – Defining a detailed plan based on practical experience
How Can We Tailor a Transformation Map with the FP&A Trends Maturity Model?
The first question to the participants was, “Is it even possible to plan for uncertainty?”.
Dev Mertia shared his view that as we live in a VUCA (Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity) world, the only way is to keep adapting and reinventing the FP&A function. Christine Fromont added that adopting a Rolling Forecast approach is an effective way to mitigate uncertainty. Paolo Guerrieri suggested that we should plan and leverage real-time scenarios while choosing the most adapted ones for the specific situation. Mikael Ciompa supported this view by sharing his experience. During the COVID-19 pandemic, his organisation prioritised Scenario Planning as the most effective tool. Larysa Melnychuk concluded that although the available technology can certainly help us solve many challenges, it is even more important to use it in a focused and adopted manner to achieve the best results.
The participants were also asked to describe a key takeaway from their experience with FP&A transformation. The answers included the following:
- Change Management/Mindset
- Leadership
- Training => Role definition
- Collaboration
- Skill development
Figure 3
The group continued with an overview of the key areas of the FP&A Trends Maturity Model, and the attendees shared their experiences.
1. Leadership
Adequate leadership skills and a visionary approach ensure a beneficial transformation framework.
2. Skills and Capabilities
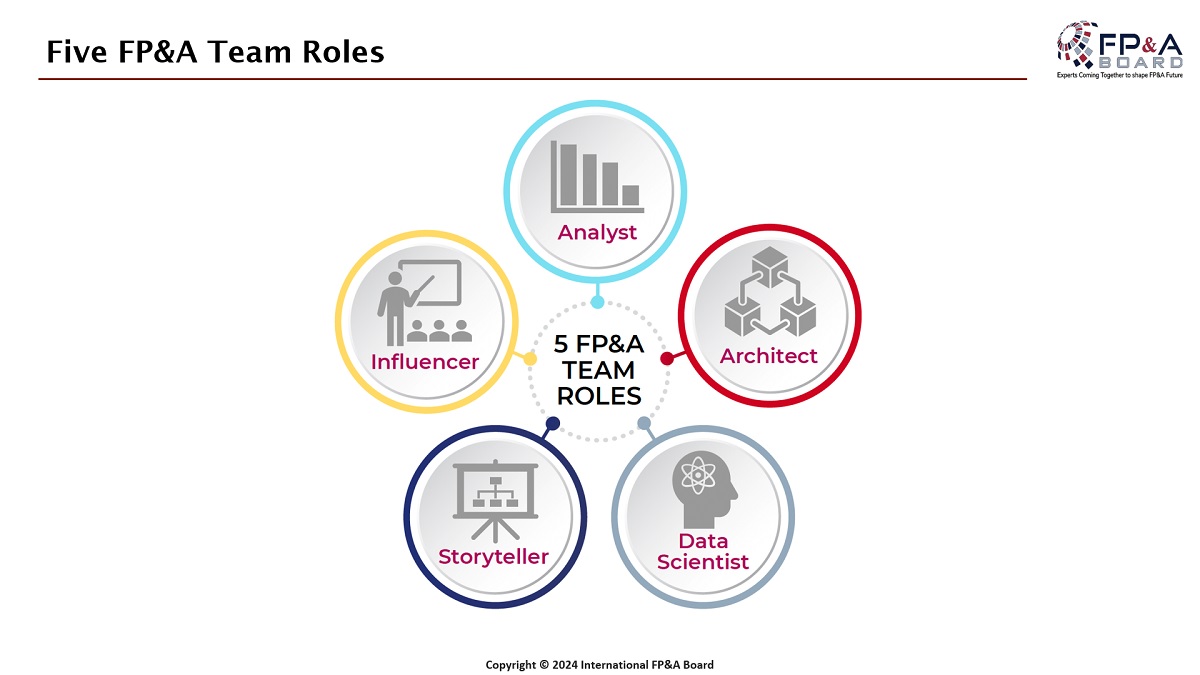
Figure 4
The essential five FP&A team roles help us understand what skills and capabilities need to be prioritised to complement a good transition.
3. Business Partnering
According to Tijana Balotic Truong, successful Business Partnering is a two-way street where both finance and the business need to walk their part to achieve fruitful results.
4. Process
Eliminating silos is key to achieving a smooth transition.
5. Data Analytics
Marie Gaffuri underlined that data clarity is a key element of the process. Anna Fastishevskaya shared a potential challenge when dealing with data complexity. Digging too much into data can become counterproductive and leave us without the capability to zoom out for the big picture.
6. Technology
Paolo Guerrieri presented some practical examples of enhancing the FP&A processes with the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Participants like Olivier Demierre, Anna Fastishevskaya and Valérie Grégoire-Gatte shared that they use AI in their organisation’s FP&A cycle to some extent. Christine Fromont exemplified these insights by referring to a dedicated AI team that was established to manage the process and build trust in the figures generated by it.
The participants also defined where they were on the FP&A Maturity ladder by participating in a quick poll. Their responses were as follows:
- 37% are in the Developing state,
- 34% are in the Defined state,
- 16% are in the Advanced state, and
- 13% have the Basic state, with no organisation at the Leading state.
It showed a slight improvement compared to the 2023 FP&A Trends Survey Results. In the 2023 edition of the FP&A Trends Survey, there were only 26% of the respondents in the Defined state and 11% in the Advanced state, with the largest share of 45% being in the Developing state.
According to Larysa Melnychuk, the Leading-state companies achieved this by consistently applying data-driven and data-informed models. AI should not be left to make decisions, but it should be used to provide the basis for informed decision-making. She summarised that the most comprehensive way of achieving enhanced agility is to create an adequate FP&A ecosystem.
Group Work Insights

Figure 5: Group work, Geneva FP&A Board №16, May 2024
At the end of the meeting, the Geneva FP&A Board moved towards group discussions to generate insights on the practical steps for reaching the Leading maturity state. The discussion facilitator asked attendees to brainstorm how to move to the Leading state. Their recommendations were as follows:
Data and Models
- Adequate data governance – invest in definition and integration and establish a Data Office
- Look for constant improvements on the go
- Manage the pace: slow is smooth, smooth is fast
- We need to explain models to stakeholders to build trust. It is advisable to run AI and human models simultaneously and benchmark the results
- Recognise people to fuel progress
Systems and Processes

Figure 6: Group work, Geneva FP&A Board №16, May 2024
Systems:
- Integrate various components, train users, develop a roadmap
- Synchronise systems to defined processes
- Adapt systems to the business model
- Establish ongoing governance framework
Processes
- Plan continuously
- Map processes against each other
- Define vision and set a time frame for it
- Standardisation and continuous improvement
People and Culture

Figure 7: Group work, Geneva FP&A Board №16, May 2024
- Define vision based on customer needs
- Ensure synchronisation of teams
- Plan resources timely and adequately
- Establish the finance function as the keeper of the single source of truth
- Align key elements to the organisational culture
- Develop adequate skills for the tasks demanded from the FP&A function
- Communicate constantly and promote the FP&A function as a reliable partner to the business
Key Takeaways
The current uncertain environment poses multiple challenges to businesses and increases the demand for improving competitiveness. Transforming organisational FP&A Maturity towards a Leading state can prove itself a true differentiator in that competition. The International FP&A Board members are called to spearhead and navigate this transformation journey by understanding its intricacies, providing adequate data and models, mastering the systems and processes and working with the right people and organisational culture.








