On March 6, 2025, the International FP&A Board gathered for the ninth time in Toronto, bringing together finance leaders from prominent organisations such as CPA Canada, University Health Network, CDW Canada, League, New Gold, LightBox, Acrisure Re, IMCD Group, Sigma One Capital and many others. The discussion centred on the evolving role of Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF) in Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A).
Larysa Melnychuk, CEO of FP&A Trends Group, opened the event by presenting key statistics from the FP&A Trends Group, outlining the agenda and inviting participants to contribute to a global research project on mastering FP&A Predictive Planning and Forecasting — an initiative already explored in multiple countries.
Sponsored by SAP, a leading provider of modern FP&A solutions, in collaboration with employment agency partner Robert Walters and global venue provider IWG, the event fostered engaging discussions.

Figure 1. The 9th Toronto FP&A Board, March 2025
Defining the Impact of Predictive Planning and Forecasting
At the outset, attendees were divided into small groups and tasked with selecting a single word that best captures the impact of Predictive Planning and Forecasting on their organisations. The most common responses included:
- Agility
- Data Integration
- Powerful and Responsive
- Forward-looking
- Partnership
- Insight
- Driver-based
These insights closely aligned with the potential impact of PPF identified by the International FP&A Board:
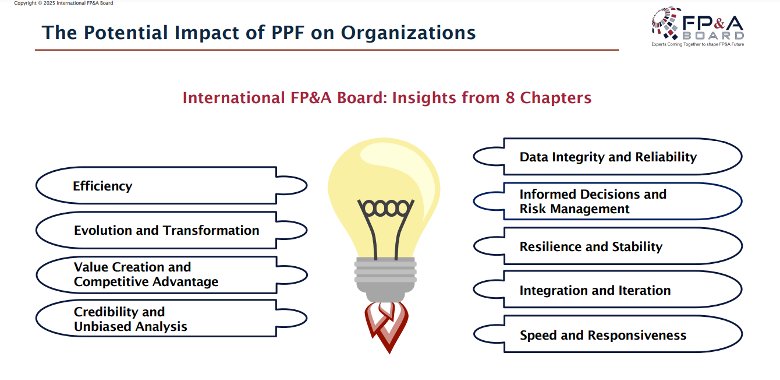
Figure 2. The Potential Impact of PPF on Organisations
Board members emphasised that obtaining meaningful insights from PPF starts with asking the right questions. Since revenue serves as a critical driver of financial performance and business strategy, organisations often prioritise revenue forecasting when implementing PPF. Accurate revenue predictions contribute to financial stability, informed decision-making and operational efficiency.
However, participants also acknowledged the complexity of PPF, particularly in relation to the “black box” effect of AI-driven predictive. Many expressed concerns over transparency, as AI/ML models often lack clarity in their internal logic and decision-making processes. Addressing this challenge will be essential for building trust through AI-powered forecasting.
The FP&A Board Members then explored the evolution of planning and forecasting, tracing its journey from traditional methods to predictive analytics.

Figure 3. From Static to Dynamic: The Evolution of Planning and Forecasting
Highlights of the Discussion
Statistical analysis is essential in the transition to Predictive Planning and Forecasting. It enables organisations to process large volumes of historical data and generate more accurate future projections.
A crucial step in this transformation is identifying and prioritising key drivers — variables that significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of forecasts. By focusing on these drivers, organisations can build more precise predictive models, anticipate changes in the market and make more informed decisions.
As one participant noted: “Transformation is a continuous journey.” A company moving from traditional forecasting to PPF focused on time frames similar to their current situation, identifying patterns to improve accuracy. He emphasised the importance of a gradual approach, continuous progress monitoring and iterative adjustments along the way for accurate results.
One FP&A Board member shared their company's experience of implementing PPF 15 months ago, still performing sanity checks. They selected 4-5 data sets, identified seasonal patterns and used regression analysis, expressing satisfaction with the results.
The Role of Time Horizons in Forecasting Accuracy
The group shared valuable insights and experiences related to their Planning and Forecasting models. Discussions revealed that organisations use varying timeframes for forecasting:
- Some organisations are still operating in the traditional stage, relying heavily on static models and extensively using Excel for their forecasting processes.
- A few organisations (~2-3) attempted to experiment with longer 18-month timeframes, but these efforts didn’t yield the desired results. They found that forecasting accuracy significantly dropped beyond a 12-month horizon, and anything beyond that was compromised by increasing uncertainty.
- Several attendees shared that they prefer using shorter timeframes - typically around 6 months — to ensure more accurate and reliable forecasts.
Overall, the discussion highlighted the importance of balancing timeframes with forecasting accuracy and the ongoing evolution of forecasting strategies in organisations. The effectiveness and necessity of Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF) often depend on the product type and industry dynamics. For example, mature products with stable demand and abundant historical data benefit greatly from PPF, while new products with uncertain demand and limited data may face more challenges. Additionally, industries with predictable cycles and long-term planning needs, such as mining, tend to rely more on traditional forecasting, while rapidly evolving sectors like technology often require more advanced predictive models to stay competitive.
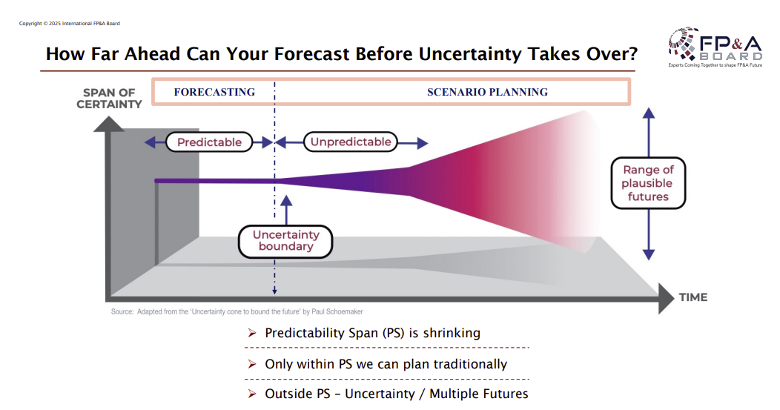
Figure 4. How Far Ahead Can Your Forecast Before Uncertainty Takes Over?
The Balance Between Speed and Accuracy in Scenario Planning
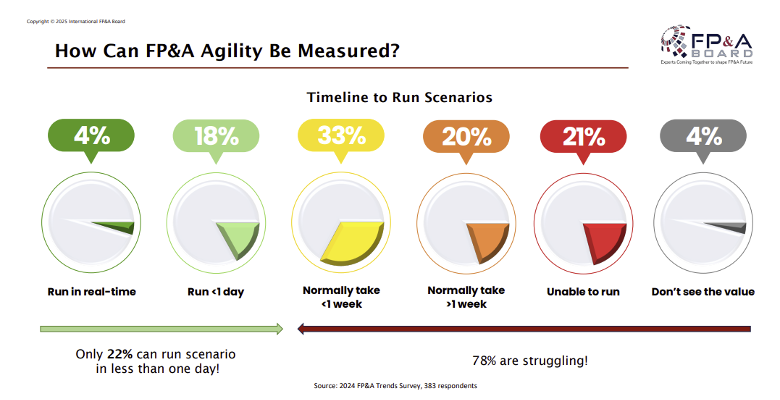
Figure 5. How Can FP&A Agility Be Measured?
These statistics from the recent FP&A Trends Survey indicate that 78% of organisations struggle with scenario agility, highlighting the need for improved speed and efficiency in FP&A practices (Figure 5).
During the session, participants voted in a live poll, providing insights into the duration of their Scenario Planning processes:
- 53% reported completing it in less than a week,
- 34% require more than a week,
- 3% perform scenario planning in real time.
While speed is important, attendees agreed that achieving accuracy is equally crucial. They also highlighted that the effectiveness of PPF depends on whether executives are willing to act on the insights it provides. Additionally, it is crucial to build trust and confidence in the models to ensure they are seen as reliable and valuable for decision-making.
Strategies to Enhance FP&A Value
The graph shows that in 2024, FP&A teams still spend 24% of their time on data collection and 21% on data validation, totalling 45%, which is almost unchanged from previous years (46% in 2023 and 45% in 2022). Although the time spent on high-value activities like driving actions (16% in 2024) and insight generation (19% in 2024) has increased since 2019 (6% and 20%, respectively), a significant portion of time is still dedicated to data-related tasks.
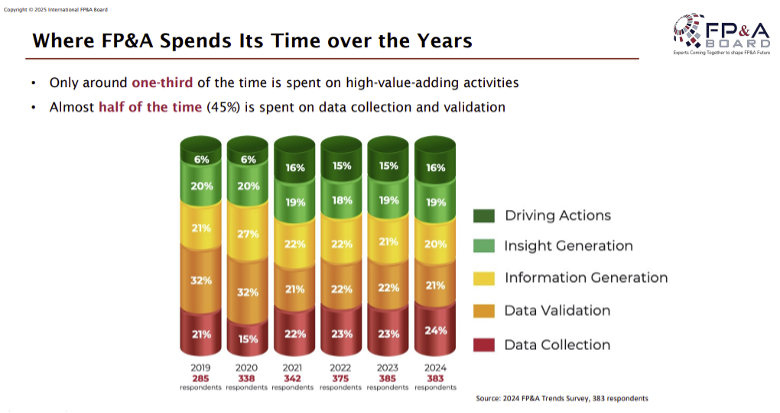
Figure 6. Where FP&A Spends Its Time over the Years
To address the challenge of low-value-adding activities in FP&A, the Toronto FP&A Board members explored strategies such as selecting the right data (internal vs. external) and enhancing driver-based decision-making. A deeper understanding of key drivers could significantly improve the quality and impact of decisions, making a real difference in driving value.
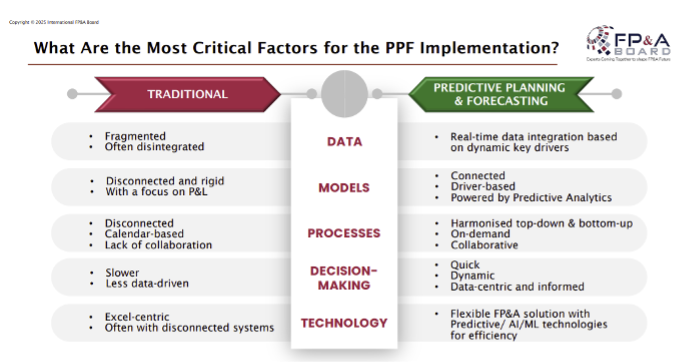
Figure 7. What Are the Most Critical Factors for the PPF Implementation?
The members identified the following key factors that contribute to improving value in FP&A:
- Data/technology
- Responsiveness to changes
- Qualified personnel — integration of advanced technologies like Machine Learning and AI into business models requires specialised skills. To effectively leverage these technologies, companies need individuals who not only have a strong foundation in data science but also understand the specific needs and nuances of the business.
- Key factor — drivers
- Human intelligence
- Business culture — organisational-wide buy-in For PPE to be effective, it needs strong support from all levels of the organisation, from executives to operational teams.

Figure 8. The 9th Toronto FP&A Board, March 2025
The group also discussed how Generative AI could be leveraged in PPE. Amneet Banga from SAP gave a short presentation on how modern technology can enhance the capabilities of business analytics, forecasting and decision-making processes. By enhancing predictive capabilities, automating report generation, and enabling more sophisticated scenario planning (based on individual products and LOBs) and what-if analysis, Gen AI ensures that businesses have deeper insights and more accurate forecasts.
Group Work: Essential Steps to Reach the Leading Stage in PPF
During the session, attendees were divided into three groups to share insights and brainstorm on essential steps organisations need to take to reach the Leading Stage in Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF). Here are the outcomes of the group discussions:
Group 1 – Building a Dynamic Driver-Based Model
This group examined how organisations can create a structured and data-driven forecasting model. Key steps include:
- Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) (e.g., revenue, EBITDA)
- Identifying key business drivers
- Ensuring data quality and alignment
- Fostering cross-department collaboration
- Continuously analysing and refining the model
Group 2 – Enhancing Forecasting Agility
This group explored ways to make forecasting more adaptable and responsive to market changes. Their recommendations included:
- Understanding current processes
- Defining clear goals
- Encouraging collaboration
- Staying agile
- Investing in talent development
Group 3 – Strengthening Technology and Analytics
This group discussed the role of advanced technology in optimising forecasting accuracy. Their key takeaways were:
- Developing a solid data strategy
- Harmonising data across departments
- Implementing advanced models
- Selecting the right tools
- Analysing key business drivers
Addressing these core areas can help organisations improve their predictive planning capabilities and move towards a more advanced, data-driven forecasting model.

Figure 9. The 9th Toronto FP&A Board, March 2025
Conclusion
Effectively leveraging predictive insights will shape the future of FP&A, enabling more strategic and proactive business decisions. As Predictive Planning and Forecasting evolves, organisations must continuously enhance their models, integrate AI, and balance accuracy with agility to drive better-informed decision-making.
The meeting wrapped up with an energetic networking session, giving participants the chance to form new relationships and engage with other business leaders.






