Why may businesses not seek out, or even resist, greater involvement of their FP&A partner? What is...
 Power of Strategic Business Partnership (SBP)
Power of Strategic Business Partnership (SBP)
There is no better approach to solving challenges than the famous saying "two brains are better than one." The financial planning and analysis (FP&A) function is evolving to meet growing demands from the business and is increasingly expected to take on a value-added, ‘business partnering’ role, to help other parts of the business improve their decision-making.
Gartner’s 2018 study suggests that the right FP&A business partnership can foster a decision-making process which could result in X% of profits. This justifies why it is so critical and how staying ahead of the competition requires FP&A to become a strategic business partner. A strategic finance business partnership would primarily focus on making the whole company stronger and would lead the finance department into a profit centre.
5 Steps Process to Evolve FP&A Business Partnering
Finance and Business - both are highly agile and result-driven functions and are symbiotically connected with a healthy P&L. To create real value, financial planning & analysis professionals need to work as thought partners with business management by demonstrating strong collaboration skills, financial aptitude, excellent business intuition, and capability to work at multiple levels to drive key strategic and tactical decisions in following areas. Here is the evolution of FP&A business partnership weighted in Business Value (Y-Axis) and Mindset (X-Axis).
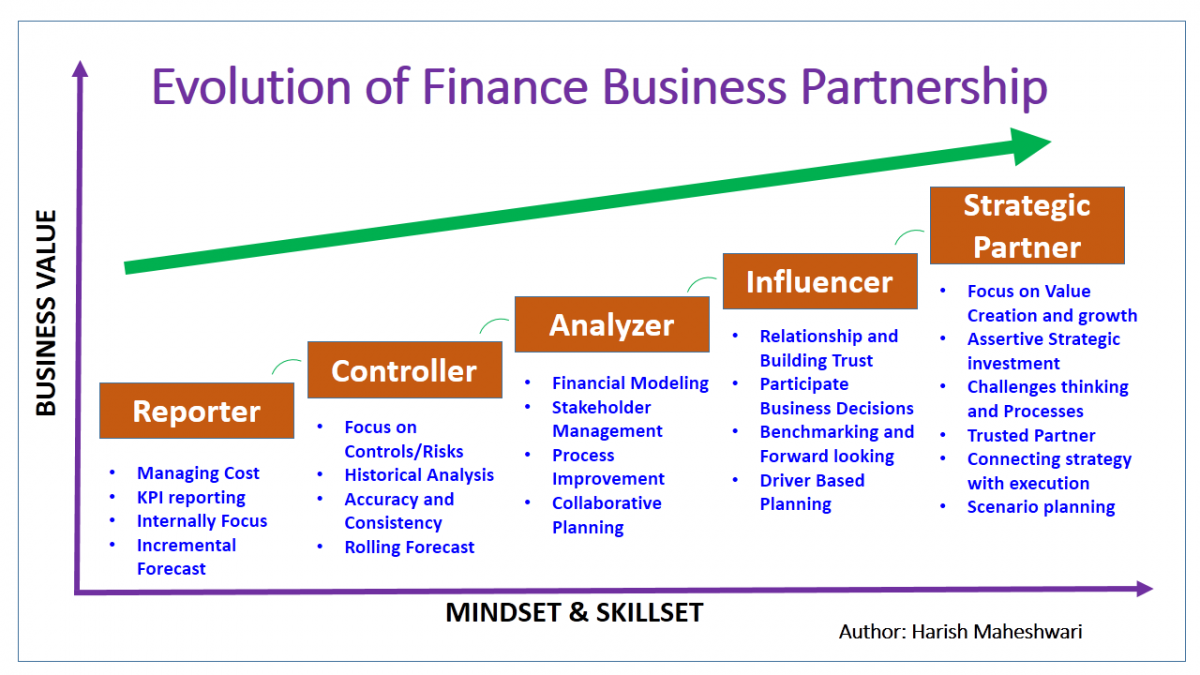
Step 1 - Reporter: Focus on bookkeeping and reporting to the business by supplying information on what is happening
- KPI Reporting: Interpret data, order and assess its value and then present the findings to the relevant stakeholders in a clear and concise way.
- Incremental Forecast: Prepare a budget using a previous period's budget or actual performance as a basis with incremental amounts added for the new budget period. The allocation of resources is based upon allocations from the previous period.
- Variance Analysis: Review actual revenue/cost against the forecast ones and determine how business performance is being impacted.
Step 2 - Controller: Focus on understanding the business and controlling the cost under budget with accuracy
- Historical Analysis: Learn from the past but stay future-orientated. Use ‘big’ and ‘small’ data, selecting the appropriate tools to manipulate, analyse and interpret it in sophisticated, audience-appropriate ways
- Problem Solving: Think logically and find solutions to difficult or complex issues.
- Rolling Forecast: Enable organisations to continuously plan over a set time horizon. For example, a rolling forecast will re-forecast the next twelve months (NTM) at the end of each quarter. This differs from the traditional approach of a static annual forecast that only creates new forecasts towards the end of the year.
Step 3 - Advisor: Focus on strong acumen and building relationships to contribute to the decision
- Communication: Simplify complexity when communicating an advanced analytics message. Communicate to executives to make sure the insight and foresight provided have an impactful effect at the executive level.
- Stakeholder Management: Work with all internal and external stakeholders. Companies with strong stakeholder relationships are more profitable and sustainable than companies whose focus is exclusively on the bottom line.
- Collaborative Planning: Use best practices in your rolling forecast process, incorporate lessons learnt and empower the finance team to actively influence day to day decisions.
- Financial Modeling: Perform a “what-if” analysis on the impact of various business decisions. Financial models represent the financial situation by taking into consideration the different business factors/conditions and risks and assumptions of the future.
Step 4 - Influencer: Focus on using the right information to influence and challenge decisions
- Relationship: Build trust with the stakeholders. Influence starts with relationships and trust. There is a direct correlation between the quality of your relationships and your influence.
- Business Performance: Influence and challenge day to day decisions across the business to ensure processes and activities are geared for maximum performance.
- Benchmarking: Analyse how your company is performing against peers and competitors.
- Driver-Based Forecasting: Promote driver-based planning on identifying an organisation’s key business and value drivers and then creating business plans and budgets based on these key drivers. The goal is highly valuable in helping executives understand the true value drivers or levers of their business, and how changes in these drivers can impact future business outcomes.
Step 5 - Strategic Partner: Focus on sharing insights and predictions to impact the strategic decisions
- Business Acumen: Understand how changes across lines of the business impact the performance of the competitive landscape, and how industrial and economic factors weight in.
- Strategic Decision: Shape strategy and the direction of the business using cross-functional leadership. Act as a key stakeholder in the decision-making process by providing risk-adjusted financial information and analysis.
- Predictive and Prescriptive Analysis: Utilise advanced analytics for unbiased forecasting, long-range modelling, and prediction of future events. Analytical modelling will deliver deep visibility into the business. These forward-looking insights give the ability to quantify trade-offs realistically in order to drive strategy, all before any decisions are actually made and implemented!
- Execution Roadmap: Drive major strategic or tactical initiatives such as cost savings or revenue optimisation projects. Act as a catalyst in driving initiatives critical to delivering the strategy.
- Scenario Planning: Promote this approach to make flexible long-term plans. Every single decision in an organisation is a choice under a degree of uncertainty. In practice, we end up basing our choices on possible outcomes and best-case predictions. Scenario planning is used to identify a specific set of uncertainties – different drivers may impact certain results – and protect businesses from unnecessary risk.
Conclusion: FP&A business partners play a key role in making sure that there is a clear link between the strategy, the priorities, the operational execution and the company resource allocation behind those priorities. A strategic business partnership has dual responsibility, which creates long-term business relationships focused on creating joint value for organisations and utilising managerial levers to maximise an organisation's profitability.
FP&A business partner equipped with the right mindset and skills can contribute to both sections of the P&L: Boosting growth by working on the strategy for incremental growth of revenue and controlling costs to improve the bottom line. A successful FP&A business partnership transforms the finance function into the profit centre.
Subscribe to
FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.







