The Amsterdam FP&A Board meeting hosted on October 2nd, 2024, brought together 44 top FP&A professionals and finance experts from diverse industries and companies, such as Unilever, Danone, Kraft Heinz, HEINEKEN, Stryker, Mars, TIP Group, Hunter Douglas, Jack Links and many others. This time, the Dutch chapter of the International FP&A Board met in Robert Walters’ office to discuss how to master Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF).
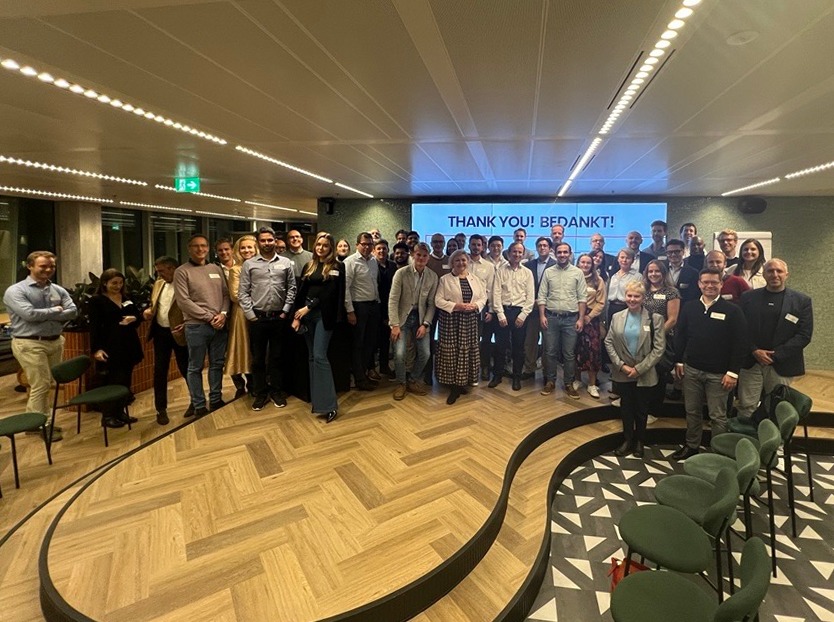

Figure 1: Amsterdam FP&A Board №15, October 2024
In this report, we are highlighting the key insights and discussions from this event, including the evolution from traditional to Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF), key prerequisites for implementation and practical suggestions for reaching the leading state.
This meeting was proudly sponsored by Workday Adaptive Planning. We are grateful to Robert Walters for their tremendous support with the event organisation and preparation.
Moving from Traditional to Predictive Planning
The attendees examined the evolution of planning approaches from traditional reactive methods to a more agile and data-driven one called Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF). While traditional methods have become increasingly inadequate for today's fast-paced business environment, PPF enables organisations to generate precise forecasts and make proactive decisions based on real-time data.
At the beginning of the meeting, the participants were asked to discuss the key benefits that may come after PPF implementation. Enhanced efficiency, adaptability, accuracy, agility, and decision-making were among the most notable insights contributed by Amsterdam FP&A Board members. Not surprisingly, these ideas resemble those of FP&A leaders in other International FP&A Board chapters where we had this discussion. On hearing a short introductory input from peers, the attendees started exploring the essentials of PPF.
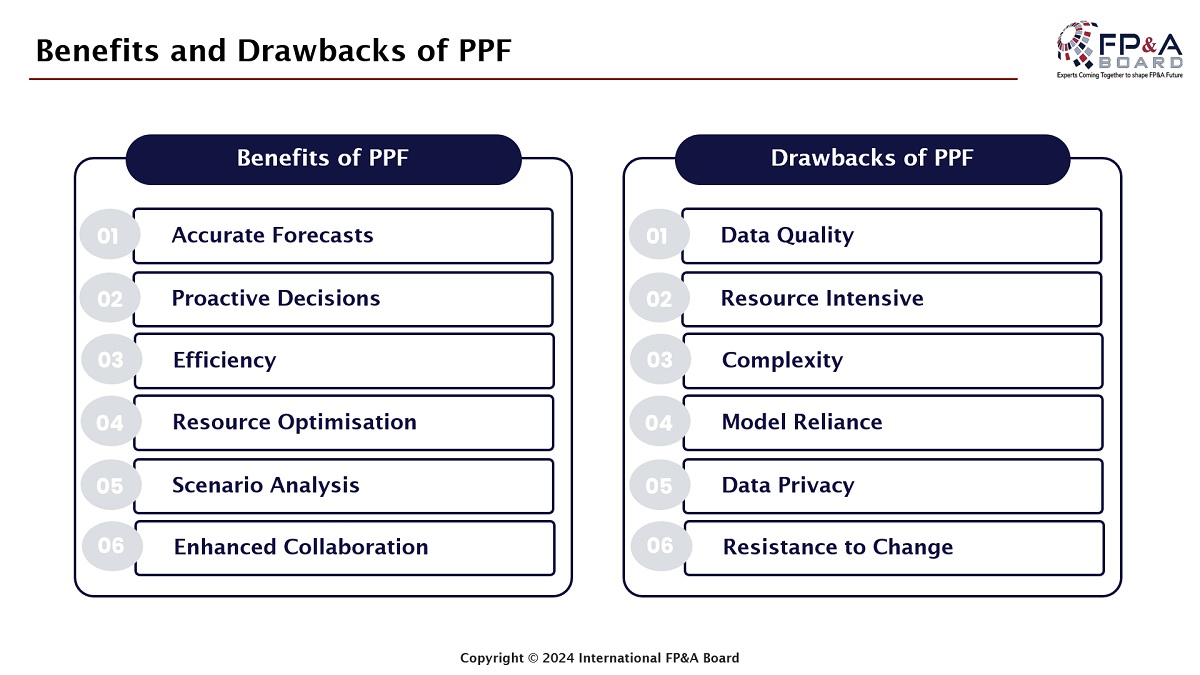
Figure 2
What Are the Key Elements of Predictive Planning and Forecasting?
The Amsterdam FP&A Board members discussed how the Predictive Planning and Forecasting framework differs from traditional rigid planning methods. The forum agreed with the detailed outline suggested by Larysa Melnychuk, who chaired the discussion.
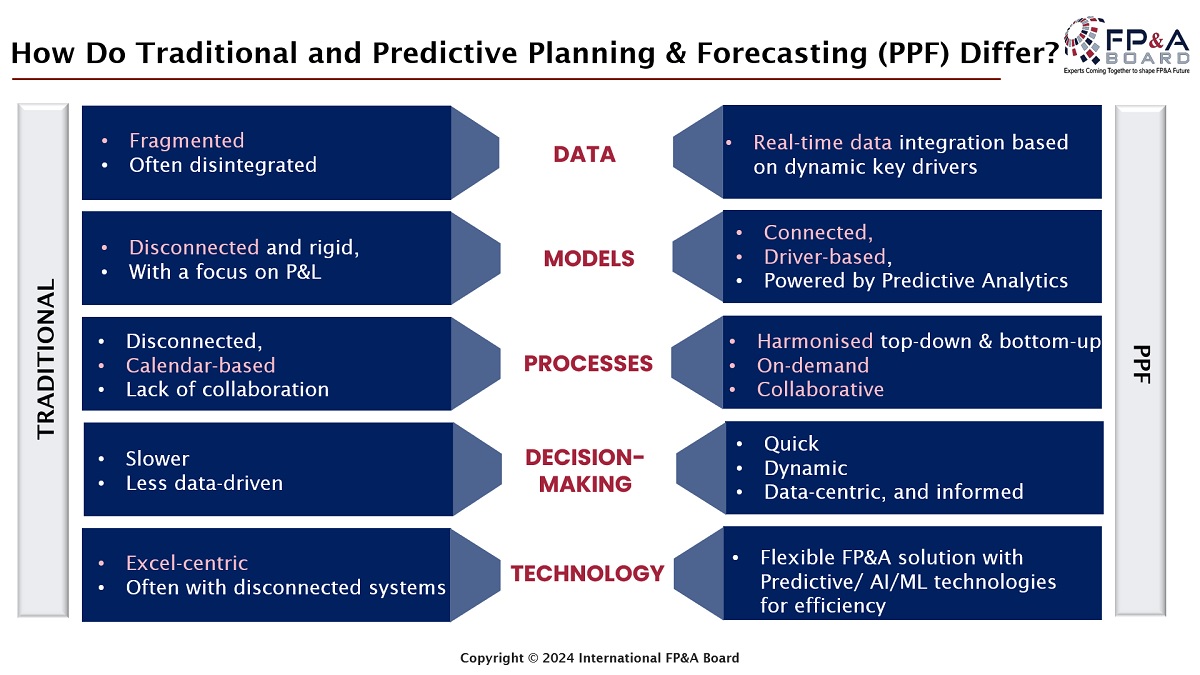
Figure 3
We also deep-dived into the emerging role of Machine Learning (ML) algorithms for empowering your Predictive Planning and Forecasting. Implementing Predictive Analytics (PA) alongside ML empowers FP&A functions to refine their forecasts with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency, promoting data-driven decision-making across the organisation and allowing access to real-time ML-driven recommendations. These insights demonstrate the immense potential of predictive techniques within diverse financial contexts.
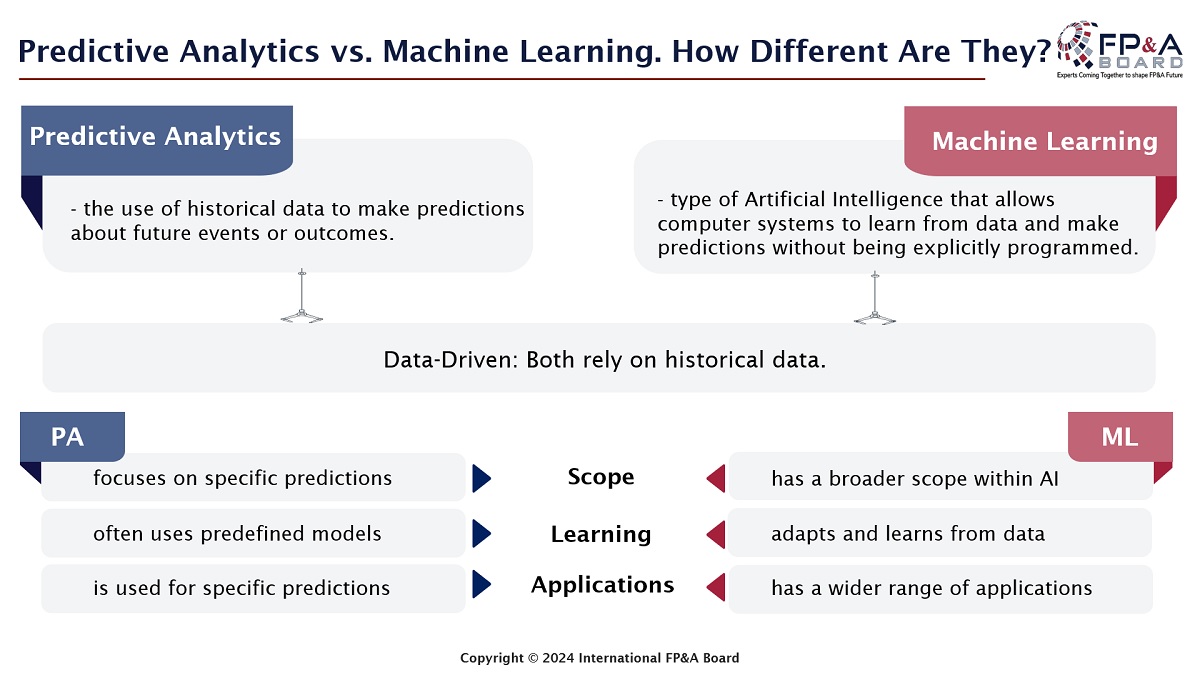
Figure 4
How to Implement Predictive Planning and Forecasting in Your Organisation
This forum also considered how to create a roadmap for the successful implementation of PPF with the FP&A Trends Predictive Planning and Forecasting Maturity Model outlined in the picture below.
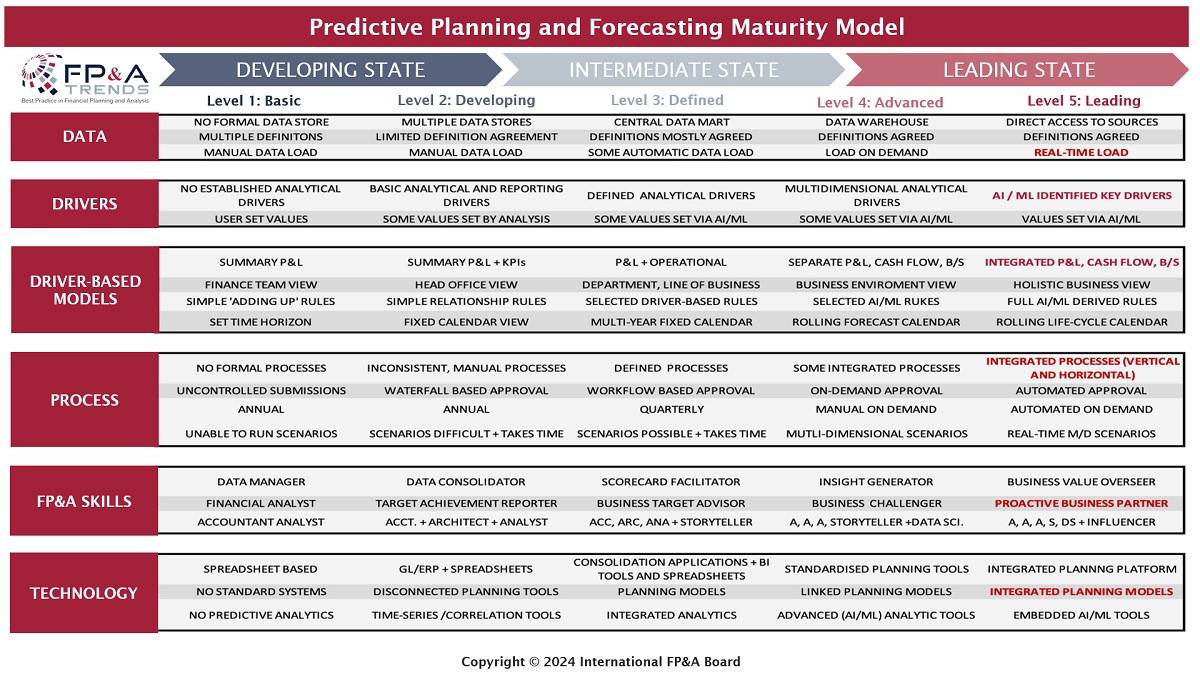
Figure 5
This model proposes a phased approach to achieving the leading stage of PPF by providing actionable insights on potential improvements across six categories:
- Data
- Drivers
- Driver-based models
- Process
- FP&A Skills
- Technology
Group Work Insights and Key Takeaways
Following a lively and anticipated discussion of the theoretical part, the group work provided invaluable insights into practical steps for implementing Predictive Planning and Forecasting (PPF).
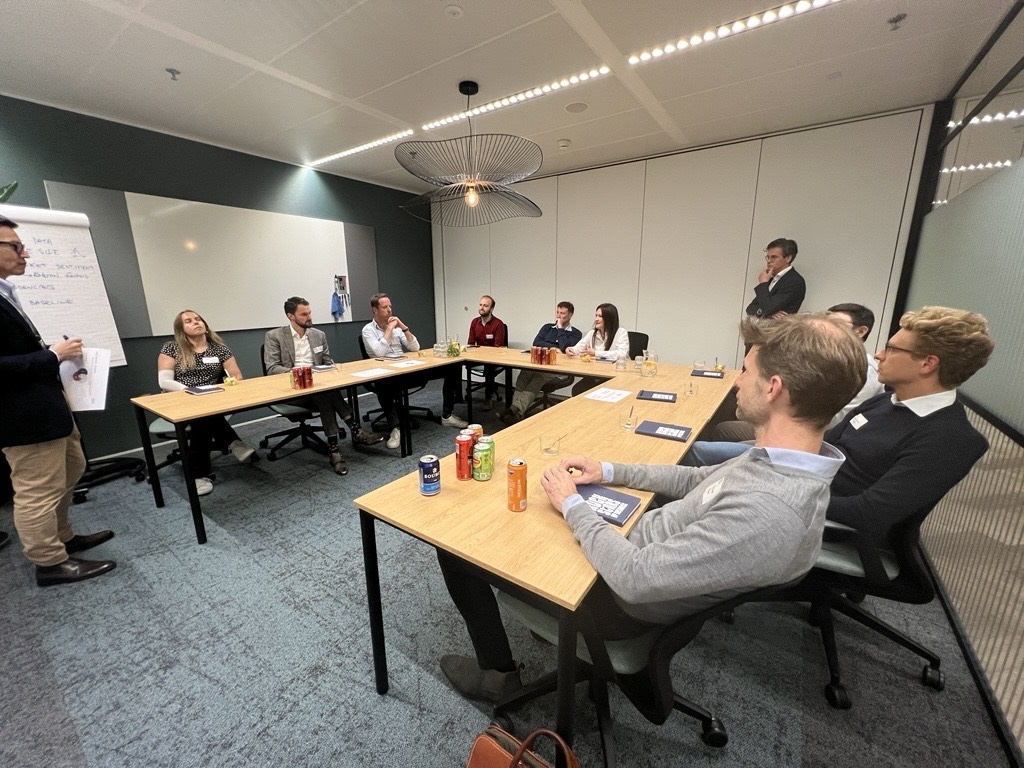

Figure 6: Group Work at Amsterdam FP&A Board №15, October 2024
The first group discussed data and models. Its participants stressed the importance of achieving organisational buy-in and validation through a trial-and-error approach, ensuring that data models can align closely with company objectives.
The second group debated on FP&A skills required for managing Predictive Planning and Forecasting. This group highlighted the necessity of strong data governance and effective bridging between finance and IT departments, underscoring the need for forging business connections and fostering a collaborative environment. They also focused on translating data into actionable stories, critical for influencing decision-making.
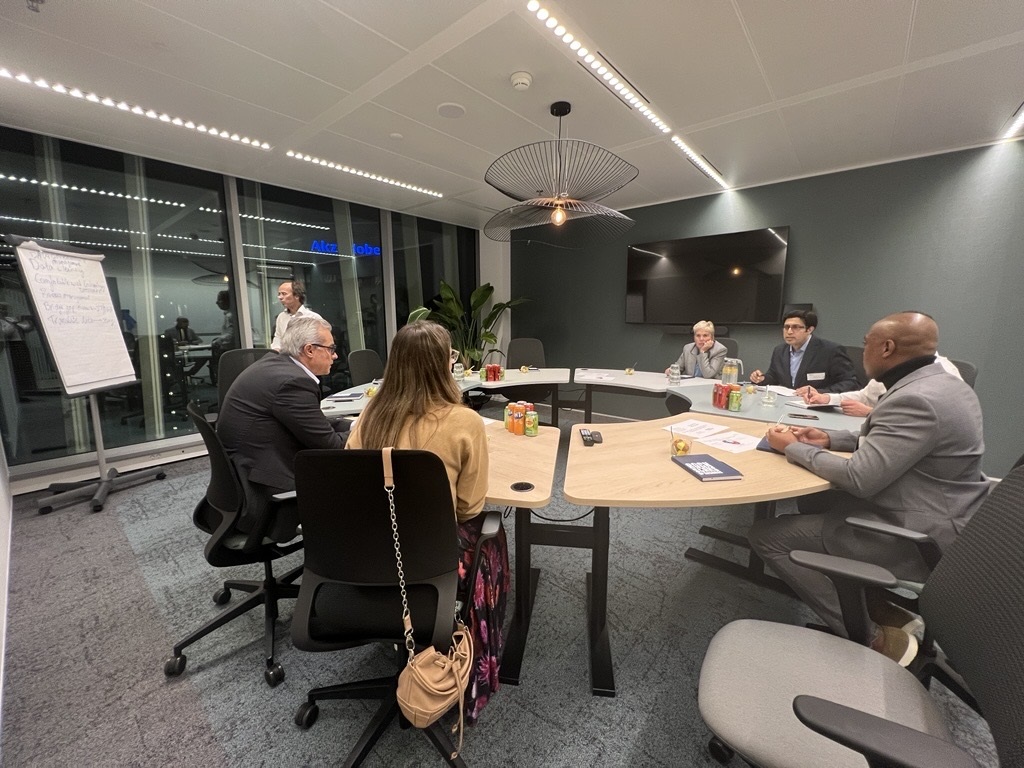

Figure 7: Group Work at Amsterdam FP&A Board №15, October 2024
Finally, the third group put technology and analytics under the lens. They stressed compatibility with advanced data lakes and the importance of iterative testing to enhance model reliability. Such insights summarise the multifaceted nature of PPF implementation, requiring attention to data integrity, skill alignment, and technological adaptability.
Conclusion
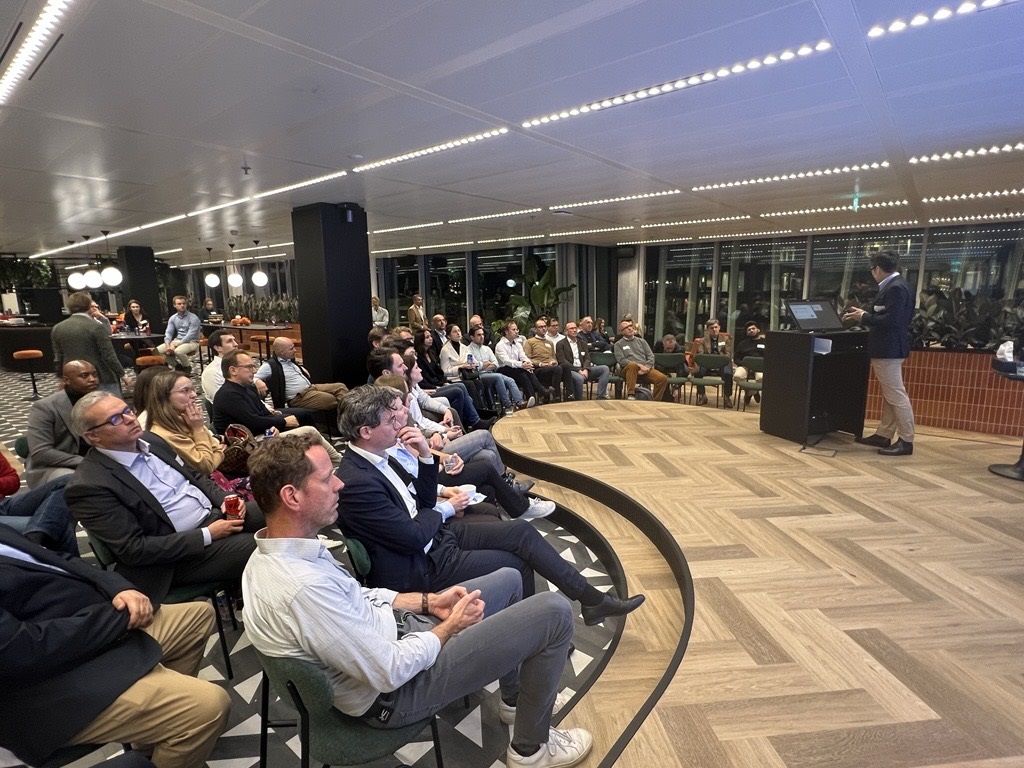

Figure 8: Group Work at Amsterdam FP&A Board №15, October 2024
The Amsterdam FP&A Board on October 2nd underscored the transformational potential of Predictive Planning and Forecasting in modern finance. By adopting PPF frameworks and leveraging advanced tools like Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning, FP&A functions can be better equipped to respond with agility to spontaneous market and environment shifts. With PPF, FP&A teams can drive organisational resilience, supporting informed decision-making that aligns with both strategic and operational goals.
The meeting ended with a lively networking, allowing participants to establish connections among their peers and share their thoughts in an informal setting.








