In this series of articles, we delve deeper into the importance of finding the right balance...

In the earlier article, we focused on understanding how strategic decision-making helps organisations drive toward their desired outcomes. However, executives and key decision-makers often struggle between optimising for growth and profitability or finding a harmonious balance. Strategic financial planning and well-defined frameworks can significantly aid management teams in building the right financial strategy and achieving a delicate balance between growth and profitability.
In this article, we will explore the Zone to Win (ZTW) framework as a proven and powerful decision-making tool that can help managers and businesses achieve this balance.
Understanding What Is Zone to Win
The Zone to Win (ZTW) framework, introduced by Geoffrey Moore, provides a structured approach that empowers organisations to strategically navigate the complexities of innovation and growth. Inspired by Moore's extensive work on technology disruptions and market dynamics, Zone to Win offers a roadmap for achieving breakthrough success in an ever-changing business environment. The Zone to Win framework's true power lies in its applicability to strategic decision-making. Organisations can effectively make well-informed choices that balance growth and profitability by aligning their initiatives with the appropriate zone.
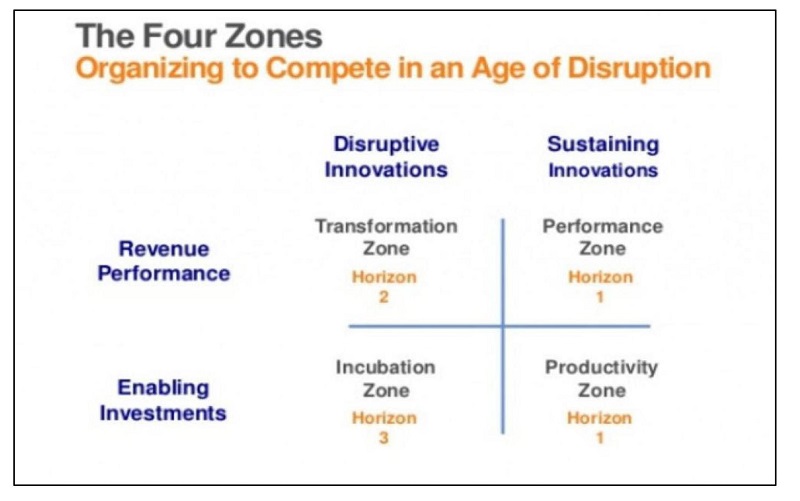
Figure 1: Zone to Win Framework. Source: Startupceo.com1
Zone to Win Framework: Understanding the Four Zones
The Zone to Win framework is divided into four zones. Each zone has a specific focus and criteria for decision-making:
-
Performance Zone
The centre of an organisation's activities is based in this zone. It includes the principal areas of the firm, goods, and offerings that generate the majority of the revenue generated by the company. The primary goal of this zone lies in maintaining and improving the financial performance of the enterprises' prevailing operations. Companies prioritise achieving comparable outcomes and maximising operational effectiveness. This guarantees the longevity of their main line of operations, which serves as the basis for an expansion.
-
Productivity Zone
Businesses concentrate on increasing operating effectiveness and reducing expenses in this zone. This entails optimising internal procedures, reducing wasteful spending, and improving operational effectiveness. Enterprises may free up assets and funds that can be committed to innovations by raising production and cutting waste during operations to propel growth strategies2. This zone facilitates the monetary freedom required to finance new ventures.
-
Incubation Zone
Innovating and experimenting are the focus of this zone. In this case, businesses create and evaluate new goods, offerings, and business plans. Organisations are urged to investigate novel prospects while taking measured risks in this area since they may spur future expansion. Even though it might not immediately boost profits, this area is vital for developing sustainable competitiveness and flexibility in a quickly evolving marketplace.
-
Transformation Zone
In this zone, companies handling major projects have an opportunity to upend the industry while having an enormous effect on the business's long-term success. The Incubation Zone's inventions and expansion prospects are expanded in this zone. The objective is to assist the organisation in achieving long-term growth by moving profitable projects into the Performance Zone right after they have demonstrated their capacity to succeed.
How to Use the Zone to Win Framework for Strategic Decision-Making?
1. Clear Strategic Focus
It offers a precise strategic focus by categorising initiatives into four distinct zones, each with well-defined objectives related to growth and profitability. This clarity enables organisations to prioritise growth-oriented efforts in the Incubation and Transformation Zones while maintaining a strong emphasis on profitability in the Performance and Productivity Zones.
2. Optimal Resource Allocation
Organisations can effectively balance their investment focus by dynamically allocating resources across the four zones. The framework ensures that growth initiatives receive appropriate attention without neglecting profitability-focused endeavours. This strategic allocation allows companies to achieve short-term financial gains while nurturing long-term growth opportunities.
3. Risk Management
It facilitates effective risk management by categorising initiatives based on their level of innovation and potential impact. Businesses can confidently explore innovative ideas within the Incubation Zone while simultaneously adopting stability and risk mitigation strategies in the Performance Zone to safeguard profitability.
4. Synergy and Sequencing
The framework encourages enterprises to identify potential synergies between initiatives across different zones. Organisations can optimise resource utilisation and achieve enhanced outcomes by sequencing initiatives strategically. This strategic alignment can help create a harmonious balance between immediate profitability and long-term growth objectives.
5. Agile Decision-Making
It empowers companies to be agile in decision-making, enabling prompt responses to changing market conditions and emerging growth opportunities. The framework supports adaptive resource allocation and strategic adjustments based on real-time performance evaluation. This agile approach also ensures a dynamic balance between growth and profitability pursuits.
6. Continuous Performance Evaluation
With well-defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each zone, Zone to Win facilitates continuous performance evaluation across various dimensions of the business. Organisations can critically assess the effectiveness of their growth and profitability strategies, making data-driven decisions to maintain an optimal balance between the two objectives.
7. Organisational Alignment
The framework fosters strong leadership alignment and transparent communication throughout the entire enterprise. This shared vision of balancing growth and profitability engages stakeholders at all levels, creating a collective understanding of strategic objectives and promoting a unified effort in executing the framework.
Practical Examples of Companies That Already Implemented Zone to Win (ZTW)
1. Amazon
One of the most compelling real-world applications of the Zone to Win (ZTW) framework can be illustrated through the case of Amazon. Their primary business, e-commerce, arguably falls within the Performance Zone, where sustained productivity improvements are essential for profitability. Simultaneously, Amazon ventured into Amazon Web Services (AWS) as an incubator project, and over time, it has evolved into a substantial revenue stream. By strategically investing in the Incubation Zone, Amazon achieved remarkable growth and eventually turned AWS into a profitable venture.
2. Alphabet Inc. (Google)
Alphabet, too, appears to have embraced the Zone to Win (ZTW) framework by exploring new opportunities while keeping Google (focused on browsing and advertising) as its primary revenue-generating operation in the Performance Zone. Take, for example, their autonomous vehicle subsidiary, Waymo, which can be categorised within the Incubation Zone. Waymo is dedicated to innovation and exploring potential expansion paths. Alphabet strategically allocates resources to incubator projects with the potential to disrupt industries, all while ensuring the sustained profitability of its core business.
3. IBM
IBM’s historical adaptability aligns with the principles of the Transformation Zone within the Zone to Win (ZTW) framework. IBM transitioned from a hardware-centric approach to a greater emphasis on services and applications. This transformation highlights the positive outcomes that can arise from operating within the Transformation Zone, including enhanced growth and profitability. IBM effectively adjusted its core business operations to address evolving technological advancements and market dynamics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ZTW paradigm provides a systematic way for companies to manage their primary operations, maximise productivity, encourage inventiveness, and scale projects that prove profitable to balance growth and profitability. This strategy assures the long-term viability of an organisation's activities while assisting enterprises in navigating the difficulties of a dynamic business environment.
References:
- BLUMBERG, Matt. "Double Book Short: Framework of Frameworks." Startupceo website. August 25, 2022. Accessed November 2023. https://startupceo.com/2022/08/double-book-short-framework-of-frameworks
- CHAKRAVARTHY, B., LORANGE, P. "Profit or Growth? Why you don't have to choose." Pearson Prentice Hall. 2008.
Subscribe to
FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.







