 This is the last article in a series of eight articles about the Operational Budget (OB) and its associated Operational Income Statement (OIS). These articles have described the significant enhancements the OB and OIS provide to the traditional budget and related financial processes and techniques.
This is the last article in a series of eight articles about the Operational Budget (OB) and its associated Operational Income Statement (OIS). These articles have described the significant enhancements the OB and OIS provide to the traditional budget and related financial processes and techniques.
All eight articles described the prescriptive Operational Budget and how it enhances related financial applications. As is illustrated in Figure 1 below, prescriptive analytics are the most powerful analytics; they can answer the question: “what is the best possible outcome?” Predictive analytics can only answer the question: “what is the outcome if we do X?”
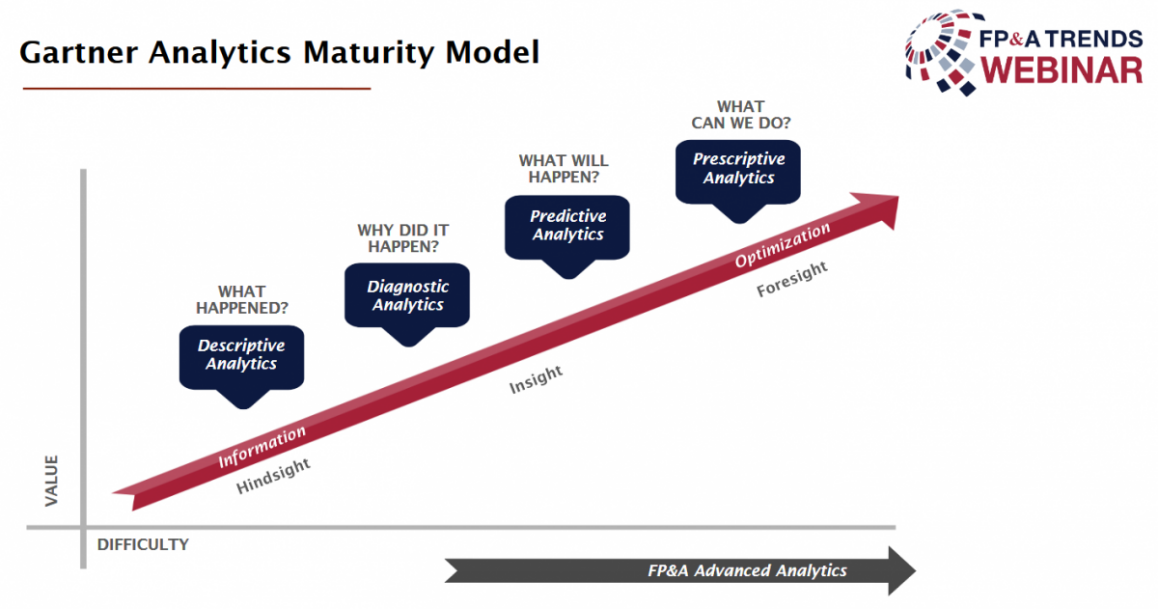
Figure 1. Gartner Analytics Maturity Model
In one of the recent Global FP&A Trends webinars, Stefan Spiegel, CFO at Swiss Railway Freight Logistics, described the use of prescriptive analytics to optimize the railroad’s whole logistics network. Illustrative of the power of prescriptive modelling techniques, he commented: “As a result, more than 25% of cost optimizations theoretically possible!”
Among the OB’s important benefits as an advanced ZBB are:
- The advanced ZBB enhances eight finance-related processes and techniques.
- The prescriptive driver-based advanced ZBB’s profit is always better than that of the predictive driver-based budget’s.
This concluding article has three sections: i) demonstrating the OB is a ZBB, ii) how the OB addresses some of the traditional ZBB’s shortcomings and iii) conclusion.
Demonstrating the OB is a ZBB
The zero-based budget is defined by Accountingtools.com as:
“A zero-base budget requires managers to justify all of their budgeted expenditures. This is opposed to the more common approach of only requiring justification for incremental changes to the budget or the actual results from the preceding year. “
The OB is a ZBB because it has nothing at all to do with the traditional budget. Further, as described in the Part 1 article, the OB is a prescriptive driver-based model of the firm’s activities with only one driver, the current forecast.
The OB’s activity-based and single driver resonates very nicely with some current FP&A articles which describe activities and drivers as the essence of a ZBB.
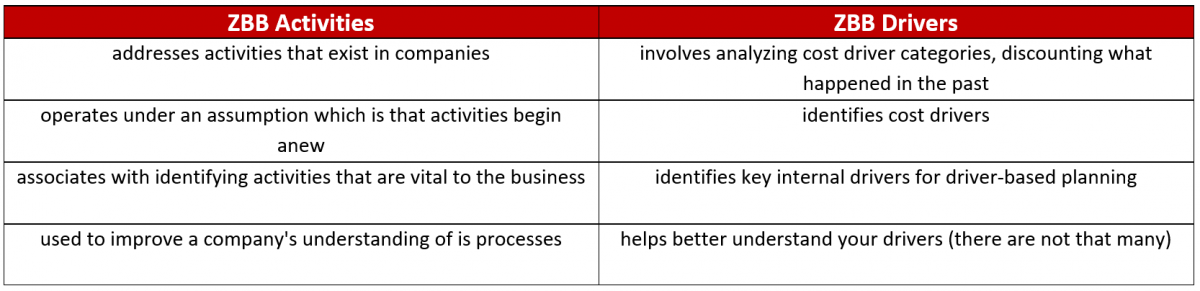
How the OB addresses some of the traditional ZBB’s shortcomings
The ZBB shortcomings listed are taken from Accountingtools.com and recent FP&A articles. Some of them are similar to those of the traditional budget (see Part 2 article for more details).
- Bureaucracy: Zero-based budgeting is a time-consuming activity that involves a lot of analysis, reporting and meetings. On the contrary, OB is a model whose structure and data have been already agreed by the relevant parties.
- Gamesmanship: Managers try to manipulate their reports by avoiding any reductions in their budgets. As described in (1) immediately above, the OB is a model the results of which are developed mathematically from an agreed-upon structure and data
- Managerial time: ZBB requires managerial time on an annual basis. There is a one-time managerial involvement to develop the OB’s structure and data. After that, there isn’t any unless the data or assumptions change as described in (1) above.
- Training: ZBB is a complex exercise that requires additional training. For the OB process, the only training required is one-time for the individual(s) working on the model’s operation.
- Update speed: Since ZBB is a time-consuming process, managers might avoid revising the budget on a regular basis. The OB is updated in real-time when any of its structure, data or assumptions change.
Conclusion
The Operational Budget 1) upgrades the predictive analytics of those planning processes and techniques depicted in Figure 2 to prescriptive analytics and 2) allows a basis for four more financial processes and techniques to be similarly updated (see Figure 3).
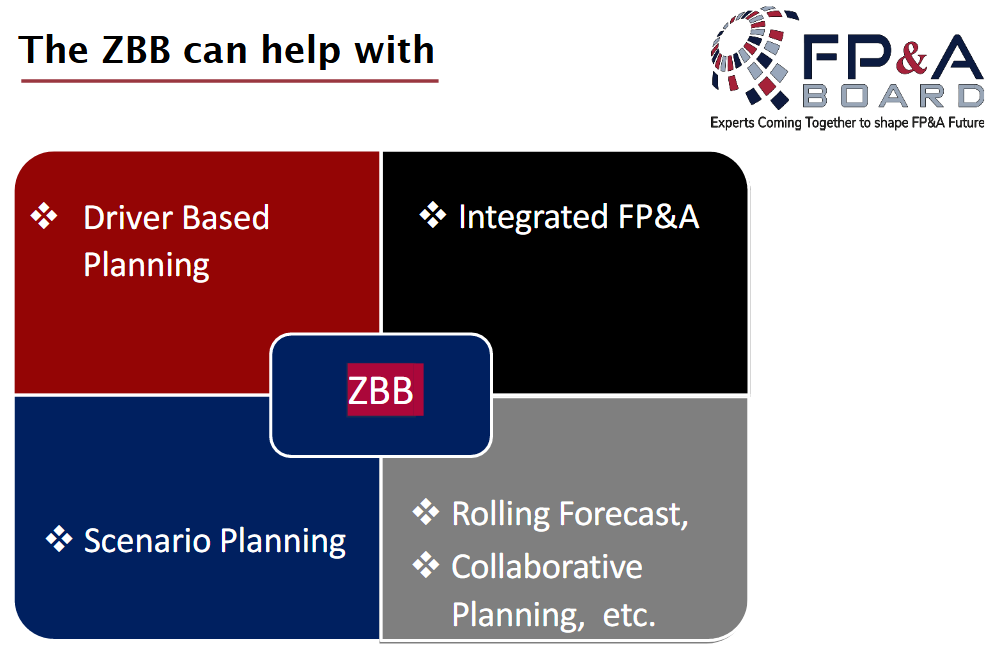
Figure 2. Zero-Based Budgeting
Articles in the Series
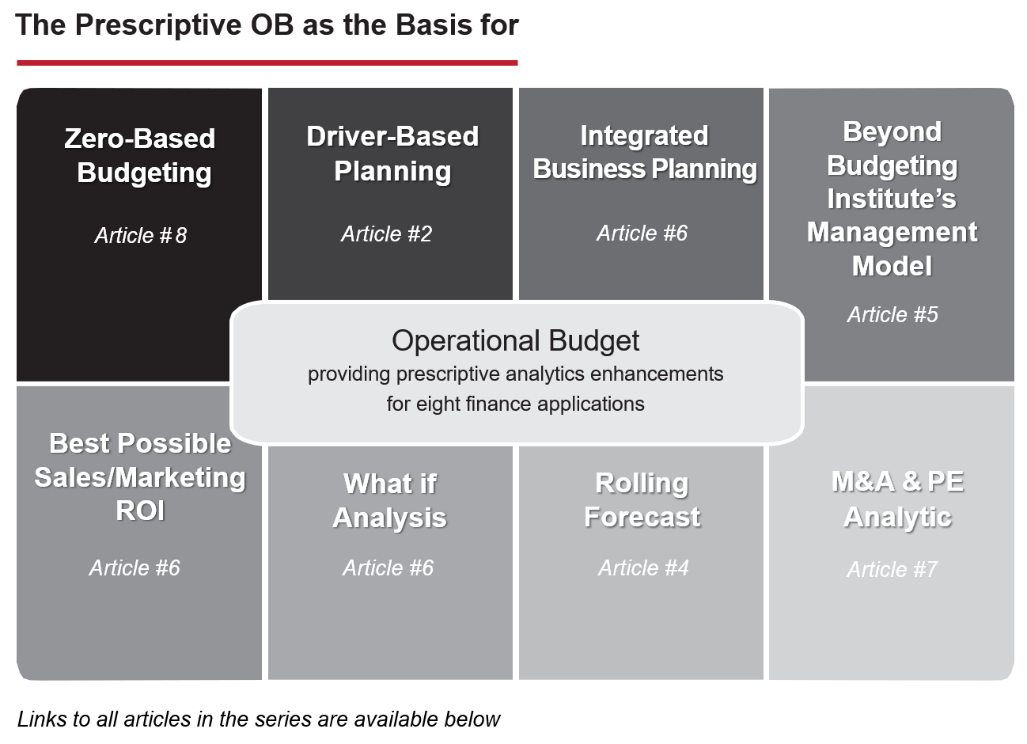
Figure 3. Operational Budget Enhancements
- Part 1: Next Generation Budgeting: More Profitable and Much More
- Part 2: OB’s benefits for the traditional budgeting process
- Part 4: OB’s benefits for the rolling forecast process
- Part 5: OB’s support for the Beyond Budgeting Institute’s adaptive management model (BBM)
- Part 6: FP&A: Uniting the Firm on a Single Planning Foundation
- Part 7: How Much Profit are M&A/PE Analytics leaving on the Table?
Subscribe to
FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.

