Irrespective of the industry you work in, I am sure all of you would have noticed...
 If there is no financial planning, there is no financial control. Since financial planning and analysis (FP&A) is connected to all departments within a business, its fiduciary duty is to secure the realised value. There are three areas where the quality of financial planning can be leveraged to maintain this value. Understanding each area will help manage real business risks and improve financial control.
If there is no financial planning, there is no financial control. Since financial planning and analysis (FP&A) is connected to all departments within a business, its fiduciary duty is to secure the realised value. There are three areas where the quality of financial planning can be leveraged to maintain this value. Understanding each area will help manage real business risks and improve financial control.
1. Accounting information
Within the organisation accounting information is the main source of information for FP&A. What information is the ‘accounting’ system producing? In an ideal scenario management receives sufficient information to manage the business well:
- A production efficiency report (or key performance indicator [KPI] report) and a cost analysis report should be available. It is not only production companies that benefit from this, but also those selling services since it is all about the ‘engine’ of the business.
- A balance sheet and income statement should be available monthly. In some countries, a signed version should be ready for a supplier to credit check the company.
- A cash flow forecast is another report that is important, even if it is just to limit the amount that family members withdraw from the company.
Due to a series of scandals and mismanagement at large corporations, new legislation was introduced e.g. Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX). Today, there is enough good practice to make sure that forward-looking statements are solid enough for external publication.
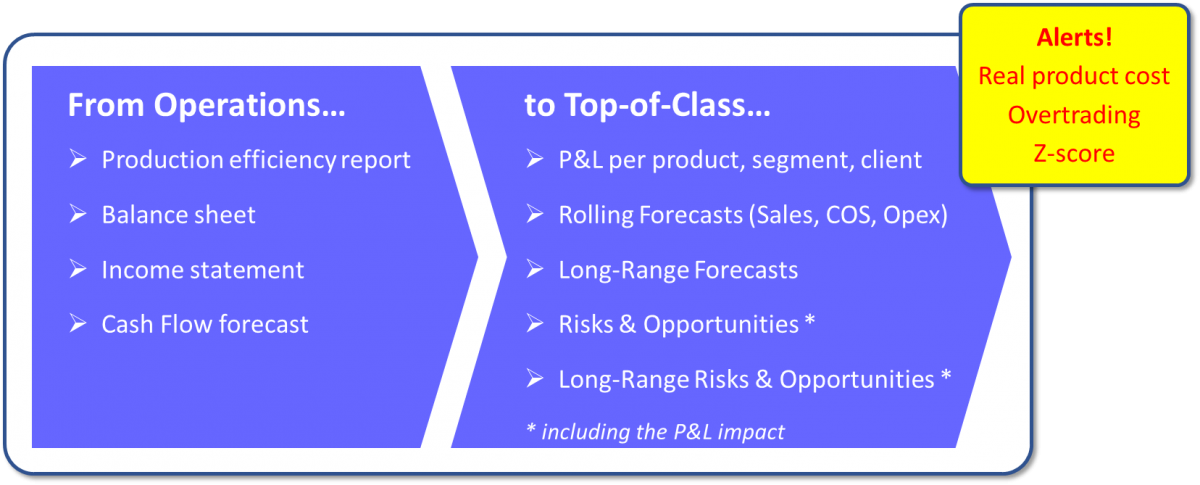
With accounting information, FP&A should be able to understand the operations and learn about its development to avoid making basic management mistakes. One company would not have built up too much inventory, leaving it cash funds low during a surprise change in demand. In another case, a company was selling at a loss because the chief engineer did not want finance to verify the product cost calculations.
2. Responding to change
From the outside, many subjects impact directly or indirectly the financial results of the company. How well does the company adapt to its environment? You want to know how effective management is when dealing with a business environment that keeps changing faster and faster. For example, when factors move in any of the following areas. Competitive, political, economic, social, technological, environmental, legal, cultural. There are a few key questions to answer that will help quickly verify the adaptability of the company.

Responding to change means managing risks. That is why companies that are top-of-their-class have finance involved in identifying risks and defining their impact on the P&L. There is always a chance that a new competitor drives the price down or enters a public bid below cost in an effort to simply gain market share. Once, a financial director of a reseller company warned the group CEO of a possible local growth slowdown, which actually happened. In this case, the global supplier was building up stock because the final customers in their key market had all started delaying expansion plans.
3. Financial function
Strong financial leadership will balance internal information with the external events that are impacting the financial results. How strong is the financial position within the business? This question is extremely normative and difficult to underpin because it involves people. At the core is decision making. Finance is supposed to question and argue for or against any major decision at the time.

This checklist will not guarantee that decision-making or change in business focus is always timely, but it does help to identify possible blind spots. In one situation, an intercompany loan in USD almost made a local go bankrupt because the head office treasury was not aware of an increase in the exchange rate. In another company the finance team instigated a change in business focus away from multi-million telecommunication contracts, that made a near-zero profit margin, to small industrial deals, that offered advanced payments and profit.
What can FP&A do?
To improve the quality of financial planning, FP&A will have to develop better services:
- Accounting information: Achieve best-in-class products and invest in analytics.
- Responding to change: Improve profit predictability and develop organisational agility.
- The finance function: Roll out finance business partnering and learn from other industries.
When these FP&A services are leveraged into the financial planning cycle, the company will be less vulnerable to competitors and management will be less pressured by its peers into making poor decisions. As such, company value will be preserved.
The article was first published in Unit4 Prevero Blog.
Subscribe to
FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.





