While the economic environment is getting increasingly volatile, processes and tools are not always available to...
 Improving financial planning and analysis (FP&A) means investing in people and systems. It is, however, good practice to map the finance and accounting processes first to see what has to change. It only takes three pages to design a process and identify new roles and responsibilities. The method below has been used to introduce new financial processes and operational reports. It has even identified a systematic risk.
Improving financial planning and analysis (FP&A) means investing in people and systems. It is, however, good practice to map the finance and accounting processes first to see what has to change. It only takes three pages to design a process and identify new roles and responsibilities. The method below has been used to introduce new financial processes and operational reports. It has even identified a systematic risk.
The Method
Before starting any change, a new strategy, vision or business model should be available. In other words, the ‘why’. It will serve as a guide and constraint for the design process. Normally one starts by mapping the ‘as-is’ situation before the ‘to be’ situation. To shorten the change process, the wishes of those leading the different financial teams can be collected to map the ‘to be’ situation. They also need to provide the conditions to make their suggestions work.
Page 1: The Process
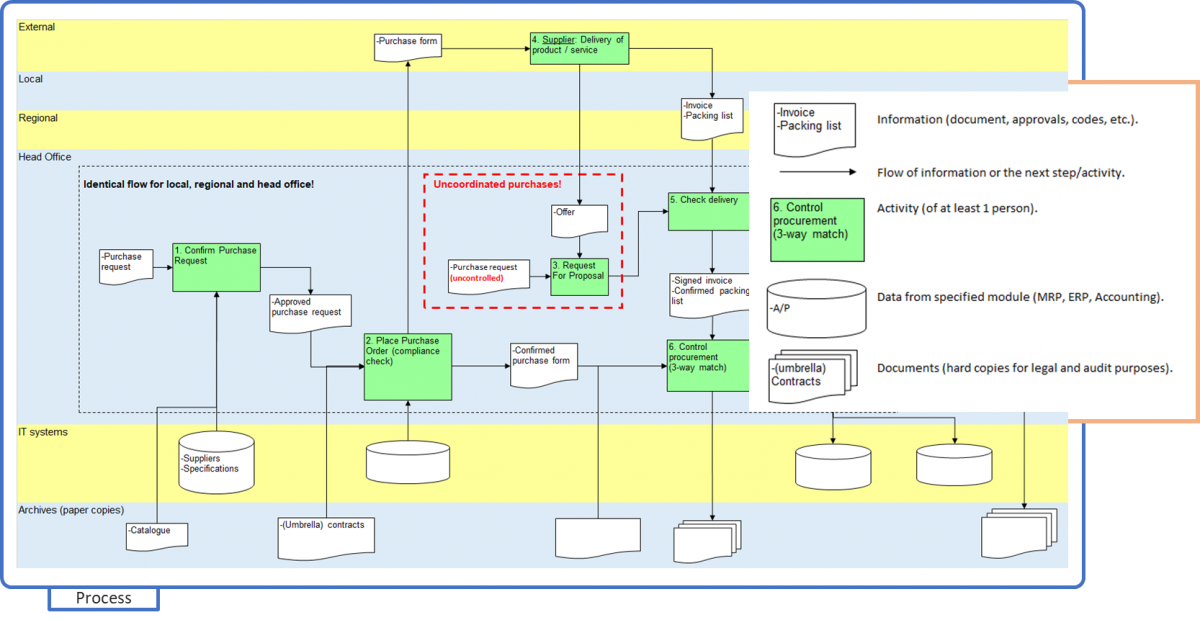
This picture contains the basic managerial structure of an organisation. In this edited example, it includes local, regional, and head office. It also shows an ‘IT systems’ level with connections throughout the process, and an ‘archive’ level to identify which documents should be saved for legal and audit purposes. Every employee, or manager, that is not familiar with process thinking or process design will understand this process flow immediately. They will often feel free to correct or adjust the process to their reality or needs.
In this example, one part occurs at all levels. The part marked in red, ‘uncoordinated purchases’, is something that happens, which could be a ‘misappropriation of funds’ risk.
Page 2: The Procedure
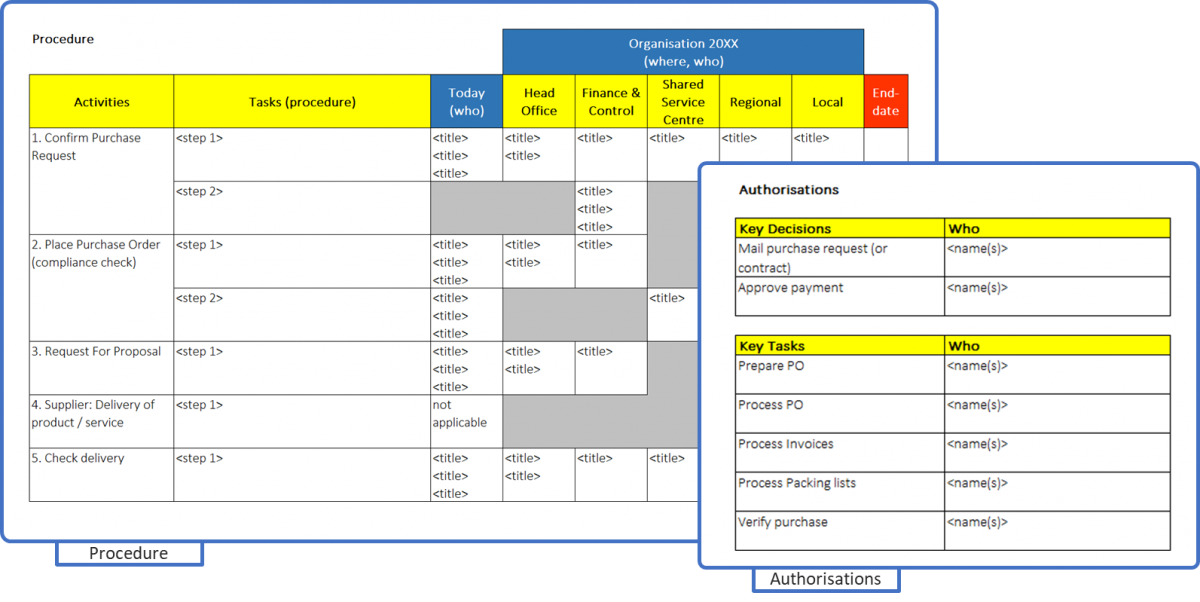
Instead of writing long formal procedures, which nobody will read, except for the writer and auditor, the main tasks are described on a second page. Every function that is doing this task can be identified too. Not mentioning names at this stage avoids politics. Describing the tasks also defines the professional qualifications needed. This is important with new tasks and activities.
Page 3: Authorisations
To complete the process design, all real authorisations are identified on the third page. Names are included here to drive accountability and reinforce buy-in. There are many formats that can be used, as long as authorisation levels are matched within IT systems and corporate roles.
Once you have mapped the processes on paper, you can start the change process by adding an extra column to the procedure sheet (page 2) called “end-date”. For each process change that needs to be made, a project can be set up and funded. This might include scheduled training, recruitment, automation, testing etc. Its operational design will make it highly useful for walk-through audits, but also for the functional design of the software.
Types of Process
Finance involves many processes. Sometimes a process is split, just to make each part fit 1 page. Finance processes in business are easier to map than those of governmental institutions. Each ‘finance stream’ has its own regulation. As a result, organisations will end up with triple the amount of processes to make sense of what is happening.

FP&A Advantages
One of the jobs of FP&A is to build business cases, not only for market opportunities but for structural efficiency improvements i.e. potential cost reductions. This method does not take much time, is easy to communicate and can help create buy-in when people affected by these changed are allowed to collaborate in improving their job. FP&A can even expand the scope to other areas:
- Risk Management or Compliance. Mapping the FP&A processes will automatically indicate any lack of control activities. Control frameworks can be complete by either matching risks with the appropriate control activity or by identifying a gap for which a project plan can be developed.
- Corporate Performance Management. It is easy to assign KPI’s to the appropriate activities. Measuring efficiencies can lead to best practices, consolidation, outsourcing of transactional services and even useful managerial reports.
- Activity-Based Costing. Extending the mapping of processes to include the core business processes is a small step. Assigning FTE’s and measuring the input or output of each activity are the first steps toward activity-based costing.
All of this work is a great opportunity for financial professionals who are seeking experience in improving the finance organisation. They can experiment, get people involved, adjust and make the process their own.
The article was first published in Unit 4 Prevero Blog.
Subscribe to
FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.





