 On November 24 I had a pleasure to participate in 3rd Digital Asian FP&A Board organised by Larysa Melnychuk.
On November 24 I had a pleasure to participate in 3rd Digital Asian FP&A Board organised by Larysa Melnychuk.
Analitical Supremacy Objective
Market competition can be seen as fast and simultaneously played chess games. The challenge comes with assessing multiple complicated situations which require tedious analysis and planning far ahead. Players with a better understanding of a current situation and possible developments have an edge to make better moves.
We all tried chess at some point in our lives. Most players are at an average level, but what would happen, if we could employ analytical tools to our advantage? Tools that would further ahead analyse all the simultaneously played games, then support every move we are about to take with the real-time scenario analysis with probabilities projections. Would that shift overall win ratio to our benefit?

FP&A Digitalisation was discussed at several FP&A Boards in the past but the recent mindset shift has changed the perspective. It went from anxiety before the implementation to peace of mind in fully controlling the processes and confidence in the quality of provided FP&A insights. The technical and psychological steps taken have been highlighted by a panel of experts, chosen from the front liners of financial technologies adopters.
Following the footprints, let’s discuss in points the steps they have taken.
Initial Challenges in Adoption
Presented by Bryan Lapidus, Director at Association for Financial Professional (AFP) and Eugenia Ng, Associate Director at Michael Page
The financial society sees the biggest challenge in corporate culture and adequate skills set (see Image 1 below). Two main reasons for this are the uncertainty of implementation effects and the fear of jobs being taken by a machine.
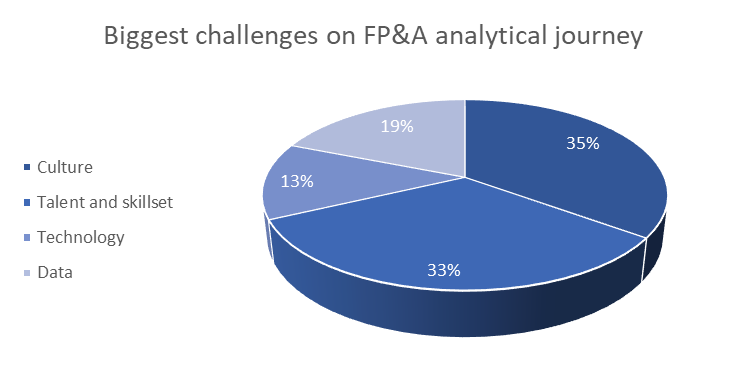
Image 1. Poll #1. Biggest challenges on FP&A analytical journey
The history teaches us that the jobs were never in shortage before or after the adoption of more advanced tools. The efficiency and the reliability/quality have been improved and new possibilities have been created. Therefore, the realistic outcome we should expect is enhancing the majority of the functions and although the least skills-required jobs will become obsolete, the economy will replace them with new ones.
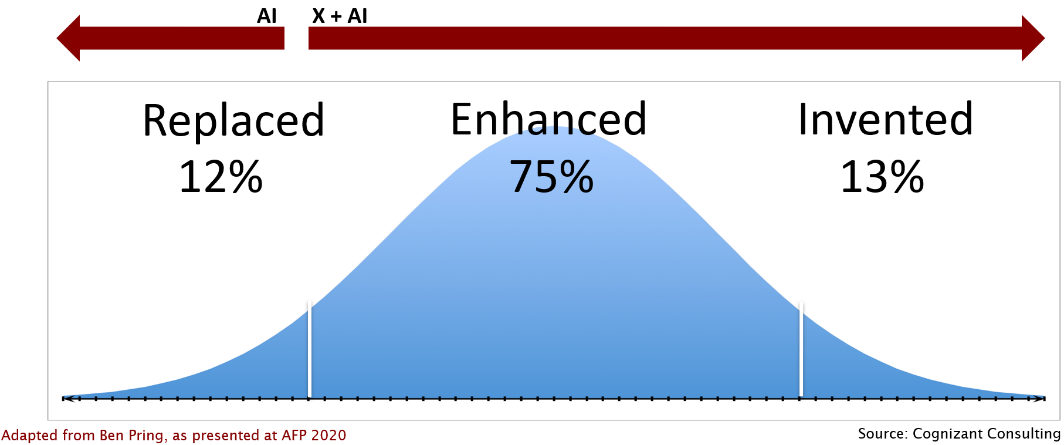
Competing with ML algorithms crushing terabytes of data in seconds and finding patterns not visible otherwise is a pointless challenge. Instead, equipped with these tools, we need to change the focus. Having more arranged and more processed information, a standard FP&A job description evolves towards more efficient communication, better collaboration on multiple organisation levels and continuous advocacy for strategically & analytically supported decision making.
This has still not become a standard. The conducted quick survey (see Image 2 below) has shown that only 22% of FP&A Teams spend more than 50% of their efforts on value-add activities, while 78% keeps being engaged in meticulous in-house work. Other survey results presented during this FP&A Board, such as CIMA Global Survey from October 2020, has also demonstrated a similar picture.
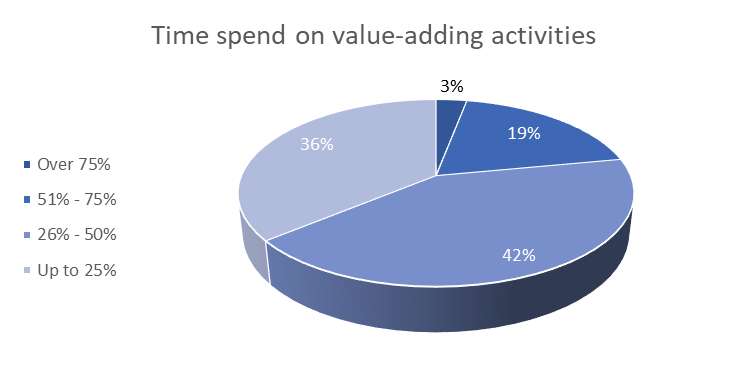
Image 2. Poll #2. Time spent on value-adding activities
The job market has already defined new skillsets. The talents understanding both technology and finance are in scarcity. As more and more companies will start embarking on the digital transformation journey, the pace will only speed up. Understanding the vision, embracing the change and developing personally cannot be put away for later. The good news is that any reader of this article or a member of the FP&A Trends community is already on his/her path.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Challenges and Benefits
Presented by Andreas Simon, Director Sales ME at Jedox
End-to-end RPA solutions are still not very common. Mostly they are used for basic tasks such as invoices and payment processing. Nevertheless, there are already advanced use cases, for example, general ledger management.
RPA is an automated rule-based program, whose objective is to remove repetitive data gathering and data processing tasks. Most companies usually use not one, but multiple IT systems, most likely different in various locations, some being more, while some less advanced. An RPA can be seen as a bridge or a patch to integrate these systems and ensure error-free workflow. The benefits include…
Short implementation cycle
Speed of impact
24/7 operations
Highly scalable
Relatively low initial investment cost
No special hardware required
To balance these benefits, companies should also consider risks and challenges. Commonly underestimated areas include current processes complexity, potential misuse risk and multidisciplinary coordination requirement. Each one of them individually can be responsible for rollout delay, lowering ROI or even project failure. Therefore, successful implementation after overcoming cultural hesitation, require forming a collaborative, can-do attitude, vision-aware team and including the following teams' representatives.
During the FP&A Board meeting, we discuss a treasury management case study for a global bank. This case highlighted the practical results after a rollout. In a highly regulated industry, bank’s treasury teams have been spending 10,000 working hour per year to manage currency and interest rates swaps, by comparing various contracts, market data, making calculations and creating and disseminating reports. The deployment of the centralised database with RPA process has freed up five FTEs from tedious updates, guaranteed compliance for each case handled and finally decreased error rate by 99.9%.
Robotic Process Automation: Advanced Use Cases
Presented by Guillaume Dubois Head of China & Asia Pacific Analysis COE at Sanofi
RPA implementation is rather a marathon than a sprint. It is a rule-based system therefore it's most suitably deployed on structured information flow directed accordingly to its parameters. The deployment process requires adaptation, change management skills and strong governance. It takes adjustments in multiple areas, such as data structuring, defining processes, redefining data accesses. Every organisation and systems it uses are continuously evolving. Complex processes are more difficult to maintain, therefore ensuring simplicity is key. Operating the RPA system requires strong ongoing governance of its integrity on one hand and on the other prompt responses from the IT teams to address fixes and changes.
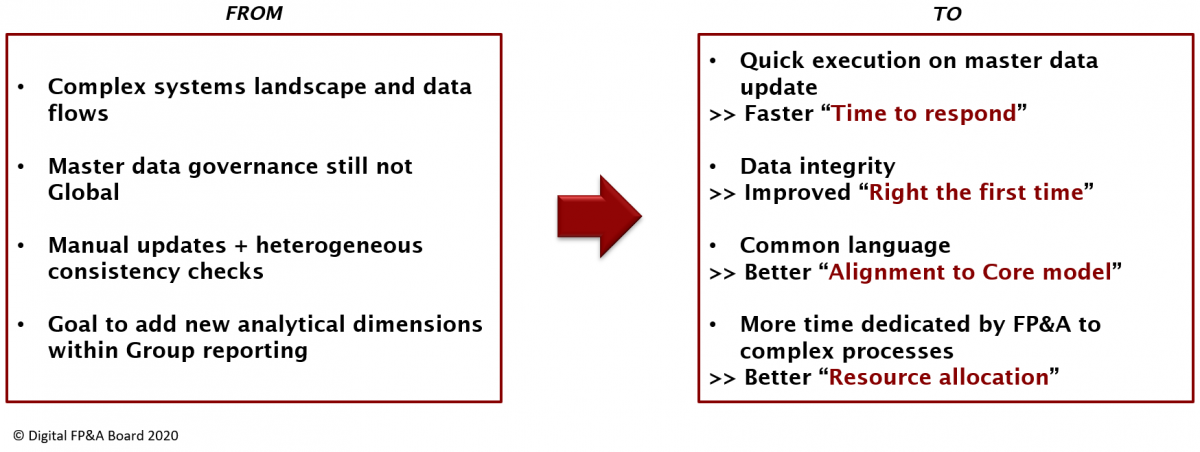
The benefits of the implementation presented on the master data file were the following.
The time to respond has improved. A single day cost centre configuration time, handled by RPA, has been decreased to five minutes. In more complex reorganisation challenges that for example require readjustments in ca. hundred cost centres take approximately two hours.
Integrity checks have been eliminated as robots operate error-free
Finance teams have been reallocated to more value-added activities. One person equipped with RPA tools remains in charge of all cost’s centres maintenance.
A poll followed by the presentation (see Image 3 below) has shown that 15% of companies have already deployed RPA, while 46% is planning an implementation. The remaining 39% doesn’t have these plans formulated, yet.
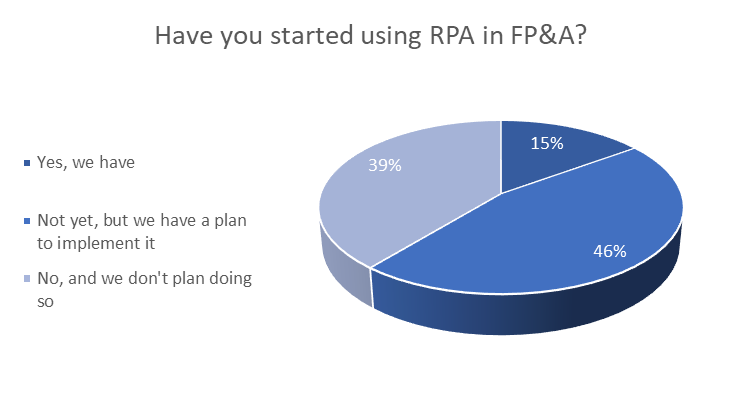
Image 3. Poll #3. RPA use in FP&A
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
Presented by Flavio Caruso Cluster CFO at Sandoz
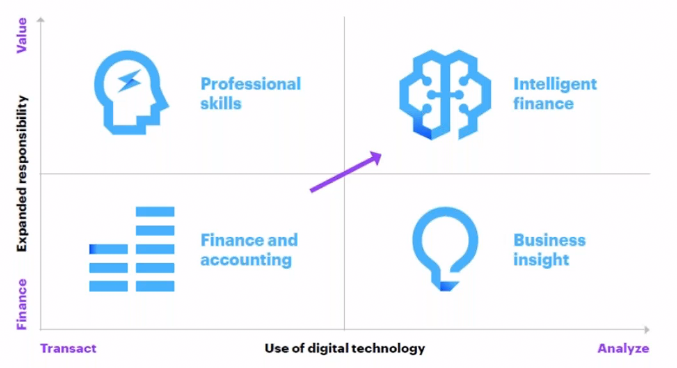
Today’s activities such as accounts receivables (AR), accounts payables (AP), cash reconciliations, inventory & fixed assets accounting, monthly closing of accounts, consolidation, reconciliation, performance reporting, tomorrow can be largely digitalised.
Finance teams can focus on strategic planning, targets setting, business advisory, performance or investments (internal or M&A) analysis. Following that Intelligent Finance vision, originated a digital transformation employing multiple initiatives and technologies.
Paperless documents processing, using RPA handling invoices bookings and supply chain.
Chatbots that provide information for employees on their performance in a conversation like manner, as a substitute for performance reports.
Blockchain solution used to guarantee classification of products distributed to company customers that would meet each country compliance needs.
Predictive analytics, application of combined neural networks, regression curves, probabilistic models, operating under objectives optimising function.
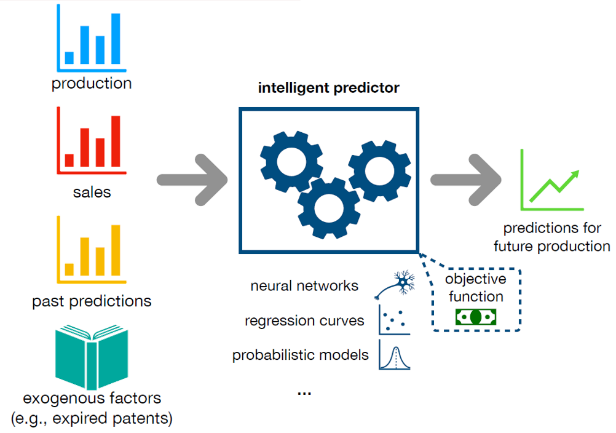
The predictive AI solutions quality testing stages started with the backtesting stage on historical data and comparison with previous processes’ derived results and variations, through parallel human and AI/ML solutions operating at the same time. Due to the higher accuracy and efficiency of the AI/ML solutions, they become the primary source of forecasts. Other benefits include reduction of COGS, stock-outs, write off reduction and less cash trapped in Net Working Capital due to better inventory management.
Such advanced solutions are still a rarity worldwide. In the fourth poll regarding the utilisation of the AI/ML in the FP&A, 24% responded they are currently using some form of AI/ML (with only 2% clearly stating they fully employ these solutions). The remaining 48% has no formulated implementation plans, as of now.
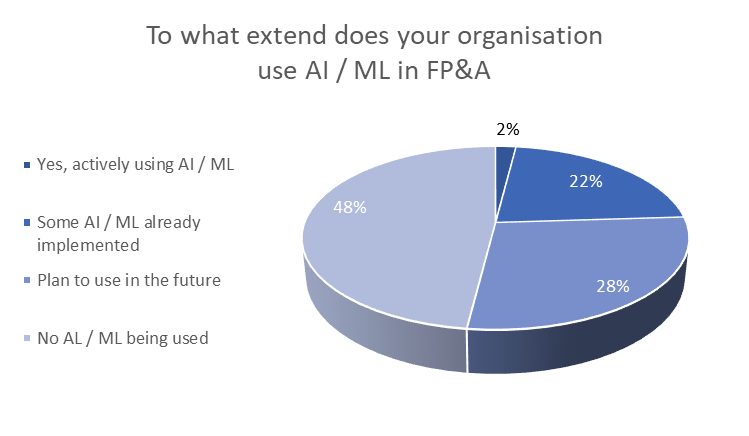
Image 4. Poll #4. AI/ML use in FP&A
Data Foundation
Presented by Khaled Chowdhury, Director of Analytics & Business Intelligence at CMC Materials
One cannot get to decision support or even decision automation advancement levels without relying on accurate and comprehensive data.
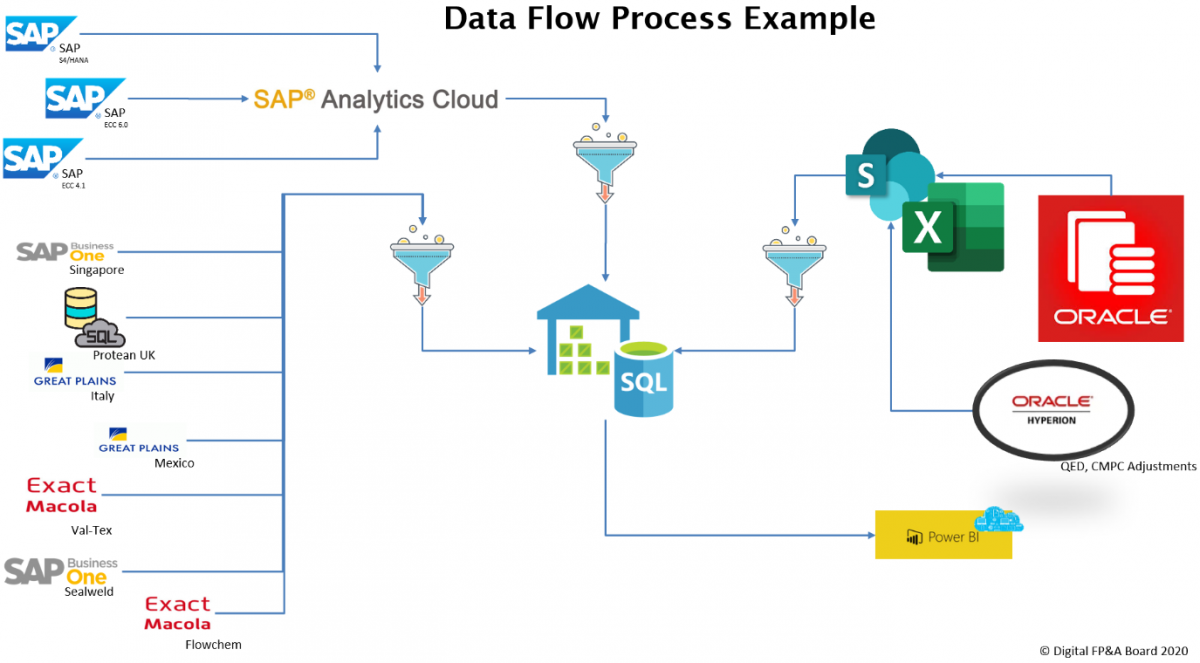
Quality of data is every department’s asset and responsibility. The data owners have the most in-depth understanding of their data, yet might lack visibility of other data’s application. Therefore, no team needs to be solely responsible for data accuracy and transparency task. As already mentioned, it’s a collaborative multidisciplinary process.
In the presented data flow process example above, data is being processed in the following steps, data generation, data preparation, data modelling and finally visualisation and communication of outputs.
Previously described use cases can be added in multiple places of the entire processes. Either as data generation tools, data processing tools or data presentation tools.
Summary
For the summary let us use the FP&A Maturity model, which is continuously discussed on the FP&A Trends Group on LinkedIn and FP&A Board meetings around the globe and clearly defines the direction and stages of an FP&A function development.
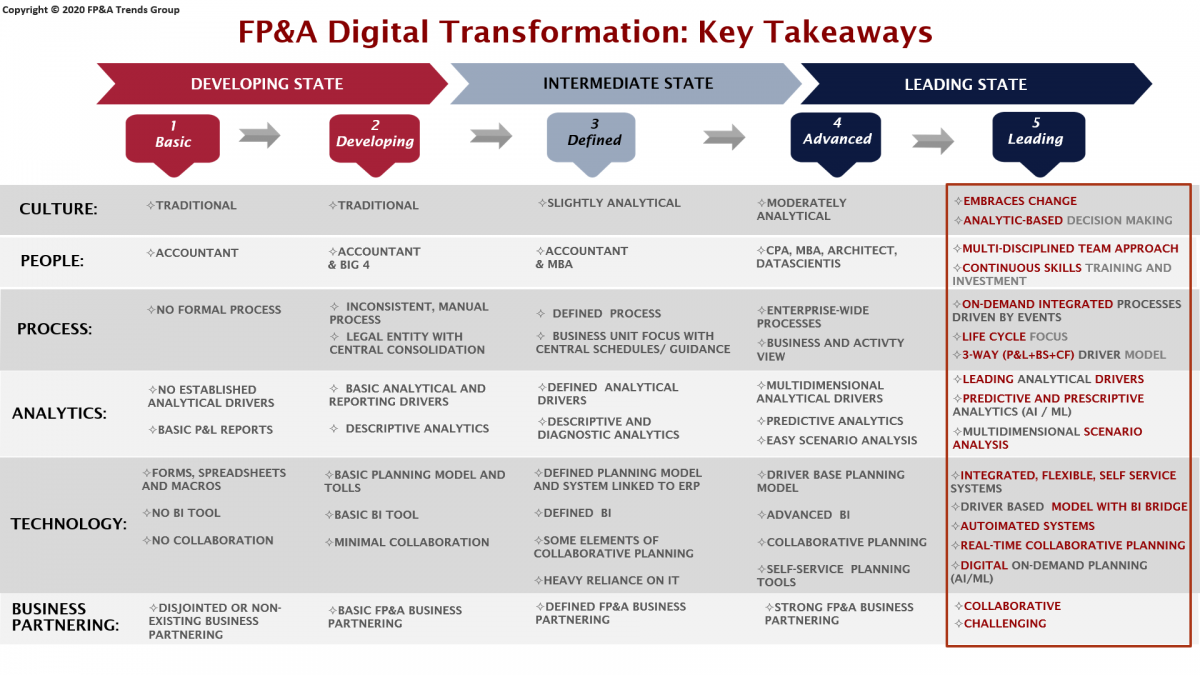
During the last three years, the attitude towards digital transformation has changed significantly and the confidence in the right move and value-added presented by early adopters is striking. The rate of adoption will only pick up in the future as the benefits will become clearer to the majority and the hesitation will change into a necessity.
We thank our global sponsors and partners, Servicetrace, Michael Page and Association for Financial Professionals (AFP), for their great support with this Digital FP&A Board.








