The Boston FP&A Board met on Tuesday, 7 October 2025, to discuss “Transforming FP&A Together: Human & AI Synergy”. Senior FP&A leaders from companies such as PTC, Takeda, Xenon Pharma, Rapid7, Pfizer, Repligen, Quadient, Sanofi, Balt, Storable and many others attended this event at IWG’s 75 State Street venue.
The event was sponsored by SAP and held in partnership with DeWinter Group and the International Workplace Group (IWG).

The agenda addressed how FP&A teams are currently adopting AI, specifically Agentic AI versus Generative AI, and how FP&A teams are setting up to enable readiness to use AI in the future.
The session also built on findings from previous Boards in London, New York, Amsterdam, and Frankfurt, continuing the international dialogue on human–AI collaboration in finance.
Some companies have become early adopters, such as Honeywell, Deutsche Bank, Microsoft and Phillips, while others are testing the waters and preparing to embrace the emerging technology for their FP&A teams.
This meeting formed part of the global FP&A Trends initiative, bringing together senior finance professionals to share experiences and practical insights on how Artificial Intelligence is redefining the role of FP&A.
Why This Topic Matters
AI is rapidly reshaping the finance landscape, yet its adoption remains uneven across organisations. The Boston discussion focused on how FP&A can leverage both Agentic AI and Generative AI to elevate analytical performance, accelerate decision-making, and strengthen business partnering.
At the same time, participants emphasised that human capabilities — judgment, ethical oversight, and strategic storytelling remain at the core of effective financial leadership. The future of FP&A depends not only on technology investment but also on cultural readiness, skill evolution, and a clear governance framework for AI use.
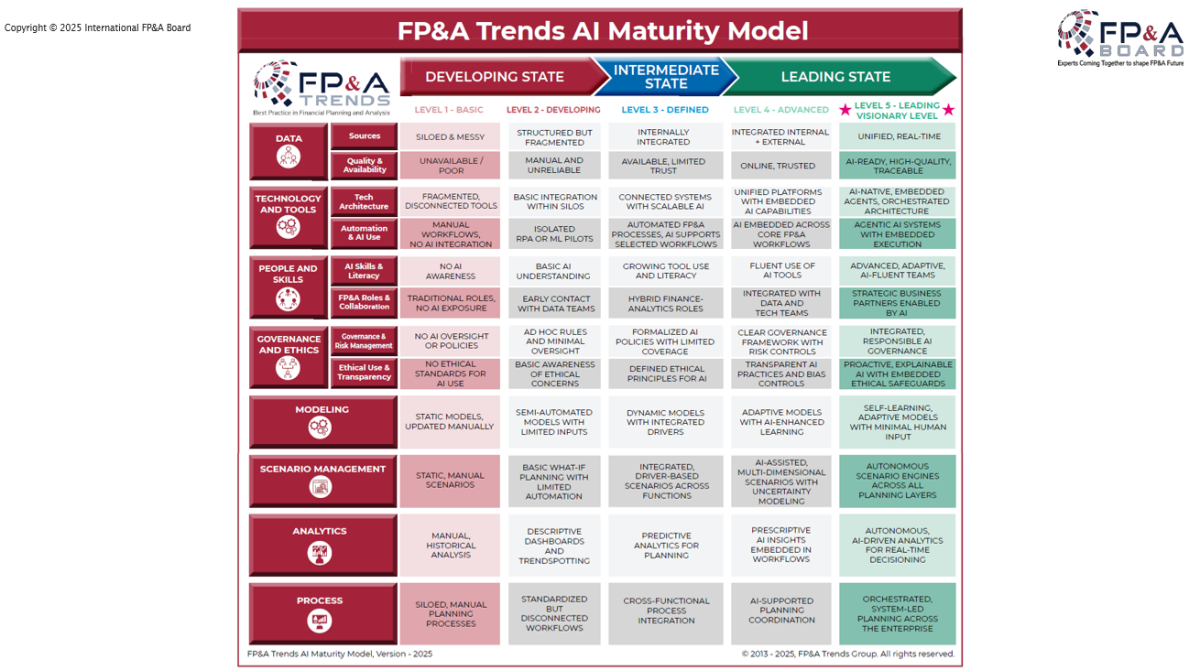
Figure 1
As FP&A becomes more predictive and data-driven, the balance between human intuition and machine intelligence will define the next generation of finance professionals.
Polling Insights
To kick off the meeting, the FP&A Board was asked:
“In one word, how do you feel about AI’s impact on FP&A?”
The group’s AI sentiment consisted of mixed feelings from participants, expressing words such as excitement, curiosity, readiness, and hopefulness, balanced by caution and trepidation.
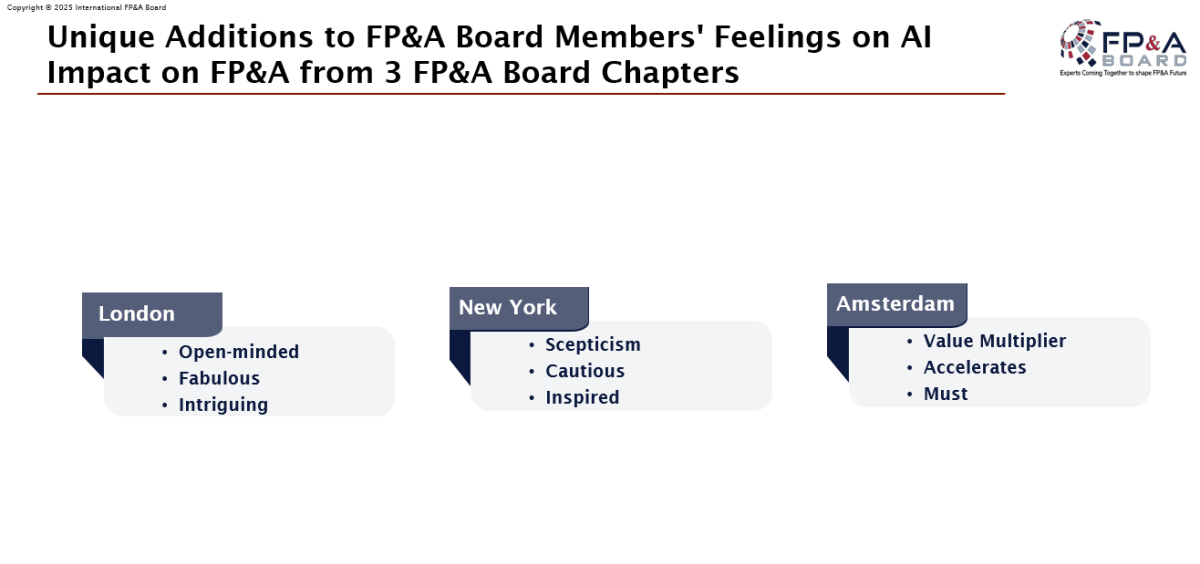
Figure 2
Next, the participants were asked to evaluate:
“How is AI currently being used within your Finance / FP&A function?”
Results from Boston indicated that AI adoption is still developing, slightly below the maturity observed at the Frankfurt FP&A Board:
- 44% not using AI
- 33% using Generative AI
- 15% using Machine Learning
- 7% using both ML and GenAI
By contrast, Frankfurt participants reported 26% using both ML and GenAI, indicating regional variations in adoption readiness.
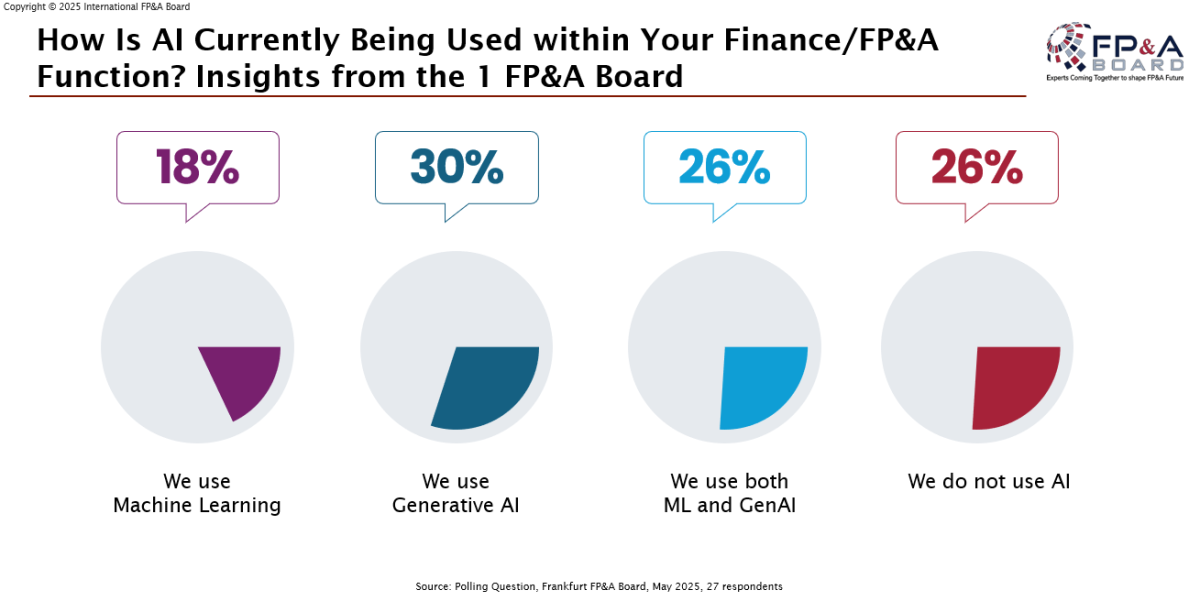
Figure 3
Key Frameworks and Discussion Highlights
Practical Applications:
The discussion included real-world examples of AI adoption from across industries and regions:
- Honeywell is using AI agents in Zurich.
- Mandarin Oriental Boston is already deploying digital “workers.”
- Coca-Cola developed a top-down AI plan distributed across business units.
- Microsoft reduced revenue planning headcount.
- SAP is working on “Business Data Cloud” to enhance data confidence.
- Saudi Arabia’s banks are using data science or a CFO with an engineering background.
- Frankfurt: successfully using ML, not Gen AI, due to Germany’s regulations.
These cases highlighted the widening spectrum of AI maturity — from isolated automation pilots to fully integrated, cross-functional AI ecosystems.
Agentic vs. Generative AI:
- Agentic AI: digital co-workers across functions to automate processes.
- Generative AI: content and scenario creation; still time-intensive for real-time use.
Barriers and Risks:
- Mid-size firms are limited by regulation and cybersecurity concerns.
- AI adoption is often hindered by data quality, cultural readiness, and regulatory environments (AI is not available in Sweden and Germany).
- Ethical and talent implications: fewer entry-level roles may challenge leadership development.
Benefits and Early Wins:
- AI increases value-added FP&A work from ~30% to ~70%.
- Tools are already improving data quality.
- “Quick wins” include automating drivers and low-risk efficiency projects.
Group Work Outputs
Participants split into three groups to discuss Generative AI, Machine Learning and Human + AI Collaboration. The findings aligned closely with those of the FP&A Boards in London, New York, and Amsterdam.

Group 1 – Generative AI in FP&A Workflows
Implementing Generative AI in FP&A begins with a strong data foundation — clean, centralised, and standardised across systems — to ensure that outputs are accurate and trustworthy.
Embedding GenAI directly into reporting and planning tools enables automated commentary, scenario modelling, and executive summaries, reducing manual effort and accelerating insight generation. When used as a decision-support partner rather than a report generator, GenAI empowers FP&A teams to deliver real-time, narrative-driven insights while freeing time for higher-value analysis, provided robust governance and human validation remain in place to maintain accuracy and trust.
Data needs to be clean, and a culture of decision-making using AI tools, rather than relying solely on reporting, should be in place to effectively implement generative AI in FP&A workflows, thereby improving reporting and decision-making.
Group 2 – Machine Learning for Forecasting & Analytics
Machine Learning can enhance FP&A forecasting by uncovering hidden trends, correlations, and early indicators across large datasets. Effective implementation begins with selecting business-critical use cases — such as revenue forecasting or demand planning — where predictive accuracy drives impact.
Integrating ML models into rolling forecasts and driver-based planning helps combine data-driven precision with human judgment, while continuous model training ensures adaptability to new conditions.
The key to success is explainability: FP&A must understand and communicate why models make certain predictions to build stakeholder confidence and embed ML as a trusted forecasting partner.
Group 3 – Human + AI Collaboration
Successful collaboration between humans and AI in FP&A requires a clear definition of roles and mutual trust. AI should handle repetitive, data-intensive tasks such as reconciliations, anomaly detection, and variance analysis, while humans focus on strategic interpretation, storytelling, and influencing outcomes.
Transparent AI tools that explain data sources and logic foster confidence, and investing in FP&A’s AI literacy ensures teams can prompt, validate, and apply insights effectively. When aligned in this way, human expertise and AI intelligence reinforce each other, creating faster, smarter, and more strategic financial planning and decision-making. This approach allows AI to focus on repetitive tasks, while humans can concentrate on the strategic components of FP&A.
The FP&A Trends Framework
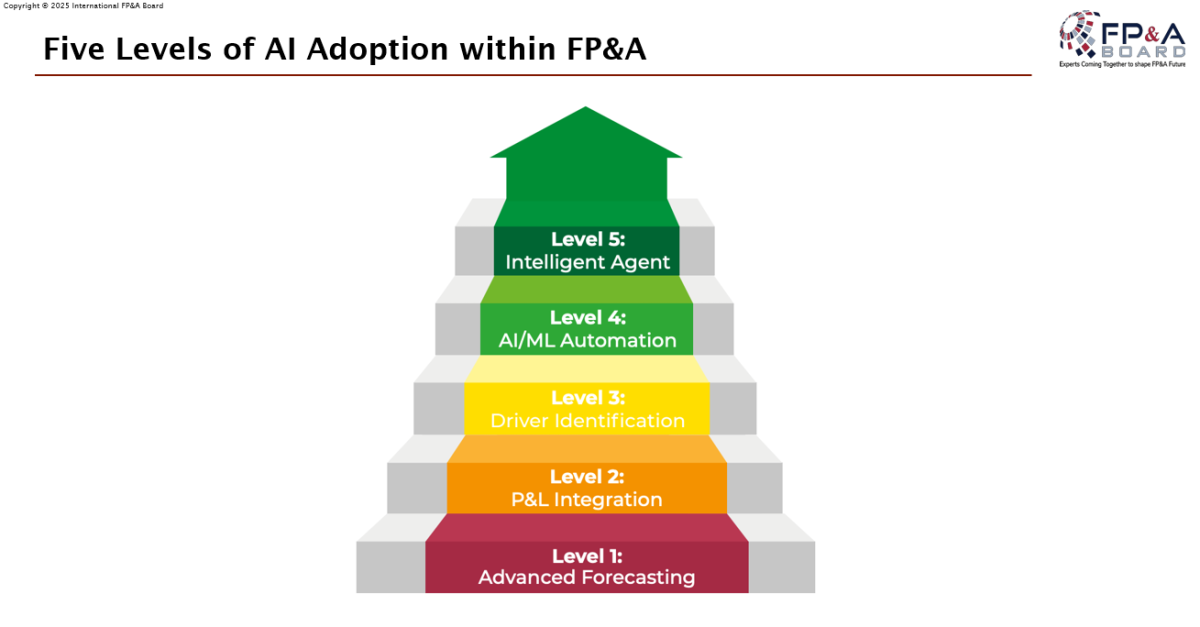
Figure 4
The discussion reaffirmed the Five Levels of AI Adoption within FP&A, where teams evolve through stages of experimentation, integration, and transformation. Early adopters are already moving beyond efficiency gains toward augmented decision-making and strategic foresight.
Conclusion
Organisations are not fully ready for GenAI, but must prepare now by embracing small-scale automation, improving data confidence, and building AI fluency within the organisation.
Companies need to be prepared to have digital workers as part of their team and embrace some quick wins once they are ready, for example, by utilising data scientists to start with simple projects, such as driver automation.
Insights & Advice:
- Future finance leaders must be multi-skilled to adapt to AI-driven changes.
- Start small — proof of concept first, then scale.
- Build readiness for “digital workers” as integral team members.
- Participate in communities like Larysa’s AI FP&A Committee (meets 4x per year).








