Introduction
The 7th Houston FP&A Board meeting, held on October 21, 2025, brought together senior finance leaders to explore the urgency of transforming FP&A practices to meet the demands of a dynamic business environment. Combined with industry research, the discussion underscored how Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping FP&A from reactive reporting to proactive, real-time decision-making.
The session was part of the International FP&A Board network, now active in 34 cities across 20 countries, and was sponsored by SAP and in partnership with Tarvos Talent.

Why This Topic Matters
The discussion emphasized the evolving role of FP&A in a world where uncertainty and rapid change demand more adaptive, data-driven approaches. The FP&A Trends Maturity Model served as the core framework for evaluating how finance teams can move from descriptive to predictive and ultimately agentic decision-making, leveraging AI and advanced analytics.
Survey data from FP&A Trends webinars (356 respondents) identified the biggest barriers to FP&A maturity:
- Technology (23%),
- Leadership (22%),
- Process (21%),
- Data & Analytics (19%),
- Skillset (15%).
Group discussions echoed these concerns, citing data challenges, technology gaps, resistance to change, and lack of alignment. Insights from 13 FP&A Board chapters reinforced the need for automation, real-time insights, and collaboration.
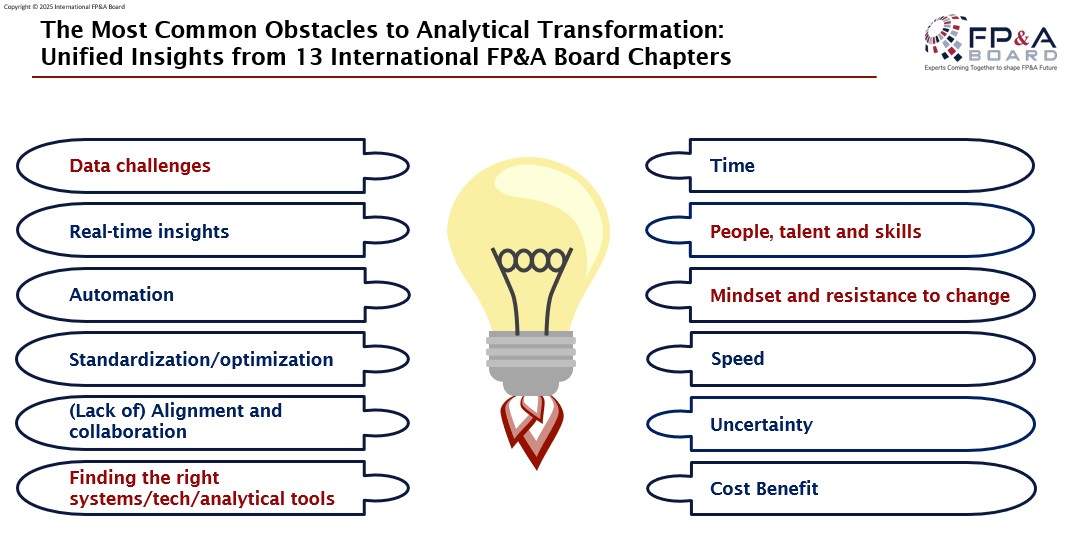
Figure 1
FP&A Trends Maturity Model
The FP&A Trends Maturity Model, created in 2016 and refined through input from 33 FP&A Boards across 19 countries, outlines six dimensions: Leadership, Skills, Business Partnering, Data & Analytics, Process, and Technology and five maturity stages, from Basic to Leading.
The model serves as both a benchmarking and transformation tool, helping organizations identify gaps and define their transformation map toward the Leading stage.
According to FP&A Trends webinars (529 respondents), most organizations are in the Developing (46%) or Defined (26%) stages of FP&A maturity. Only 2% have reached the Leading stage, underscoring the opportunity for growth and benchmarking.
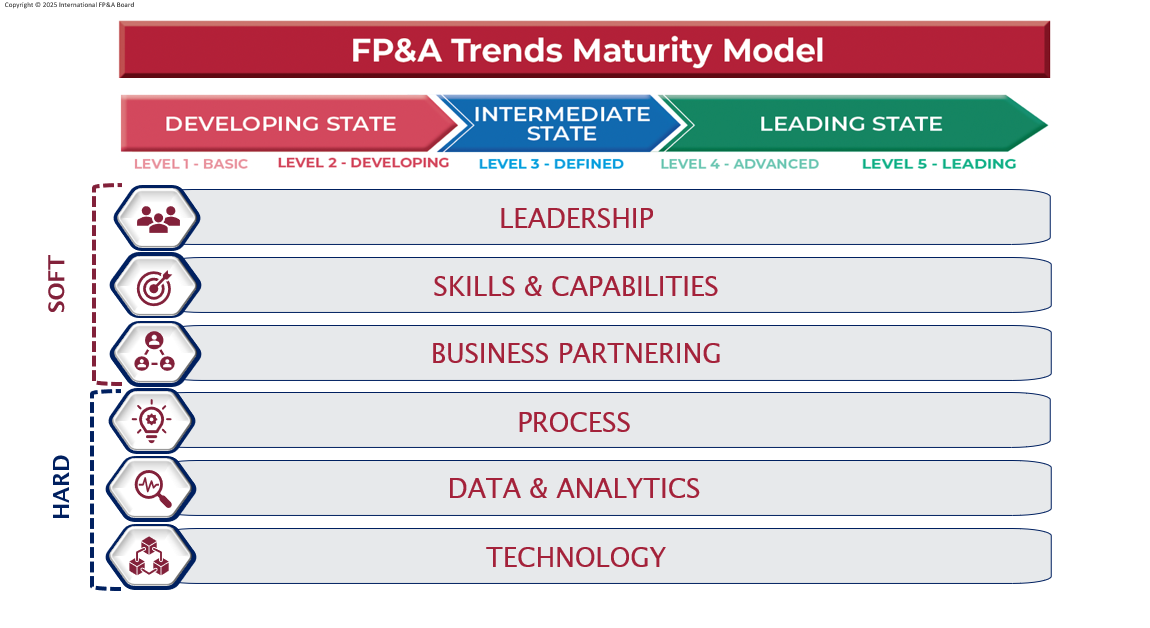
Figure 2
Three Roles of AI in FP&A
Artificial Intelligence is redefining FP&A by enabling smarter, faster, and more strategic operations.
Productivity enhancement comes from automating repetitive tasks such as data integration, cleansing, and report generation, freeing teams to focus on value-added analysis.
Insight generation leverages Machine Learning to improve forecast accuracy and uncover hidden drivers of performance, while natural language interfaces democratize access to insights across the organization.
Decision support and simulation allow finance teams to run real-time scenario models and apply prescriptive analytics, ensuring decisions are based on robust, forward-looking data rather than static assumptions.
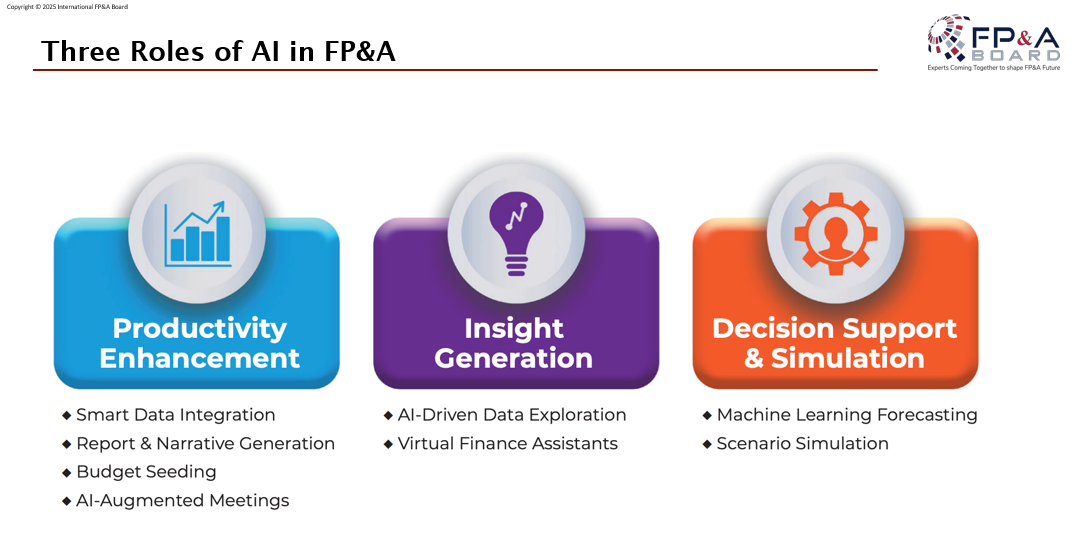
Figure 3
Scenario Agility and AI Adoption
Agility in scenario planning remains a challenge. Only 18% of organizations can run scenarios in less than one day, while 82% struggle with longer timelines.
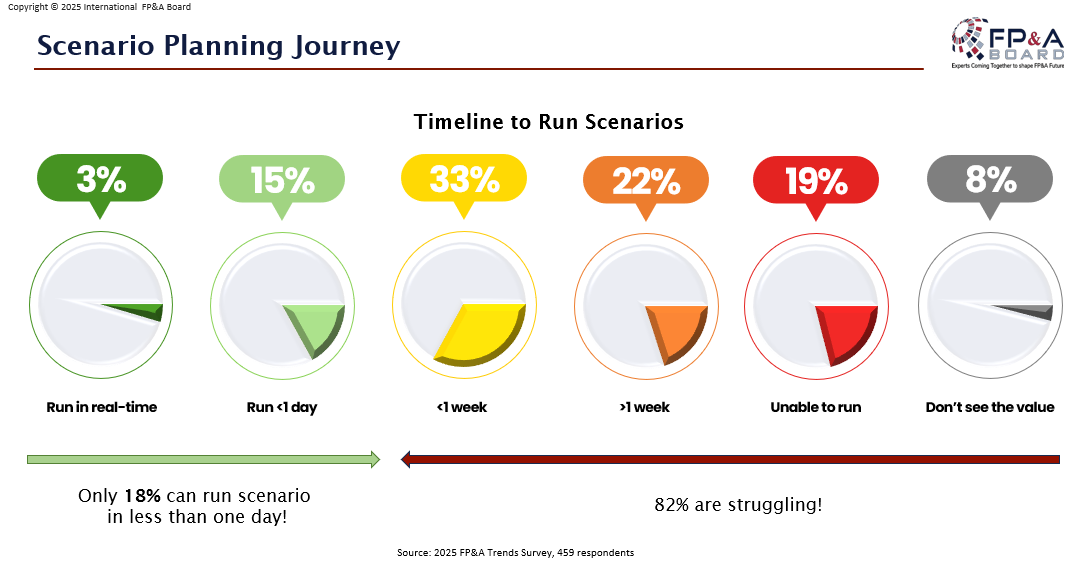
Figure 4
Adoption of AI and Driver-Based Models
Polling insights (from Frankfurt, Boston, and San Francisco FP&A Boards) revealed that:
- 15% use Machine Learning
- 30% use Generative AI
- 19% use both
- 36% still do not use AI in FP&A
Furthermore, driver-based model adoption remains uneven:
- 2% use dynamic AI-supported models
- 15% use fully driver-based models
- 40% use partial models
- 12% have not adopted them at all
Performance Gains from AI
The benefits of AI adoption in FP&A are measurable and significant. Organizations using AI/ML for forecasting report a 73% rating of their forecasts as 'great or good', compared to 42% among non-users. Best-in-class FP&A teams spend 39% of their time on high-value activities, versus 30% for those without AI, indicating a clear shift from transactional work to strategic influence. These improvements result in faster decision-making cycles, more effective resource allocation, and stronger alignment between finance and business strategy.
FP&A AI Maturity Model
The FP&A AI Maturity Model shared during the session provides a roadmap for transformation:
- Basic: organizations rely on manual workflows and siloed data, which limits agility.
- Emerging: they adopt predictive analytics and driver-based forecasting, laying the foundation for more dynamic planning.
- Advanced: introduces AI-based predictive planning, integrating Machine Learning into core processes.
- Visionary: represents the pinnacle of maturity, where autonomous scenario engines and self-learning models enable continuous, adaptive planning.
Critical Enablers
Achieving AI-driven FP&A maturity requires more than technology — it demands leadership commitment, robust data governance, integrated platforms, and cultural readiness. Upskilling teams to develop AI literacy and enhance business partnering capabilities is crucial for effectively interpreting insights and influencing decisions.
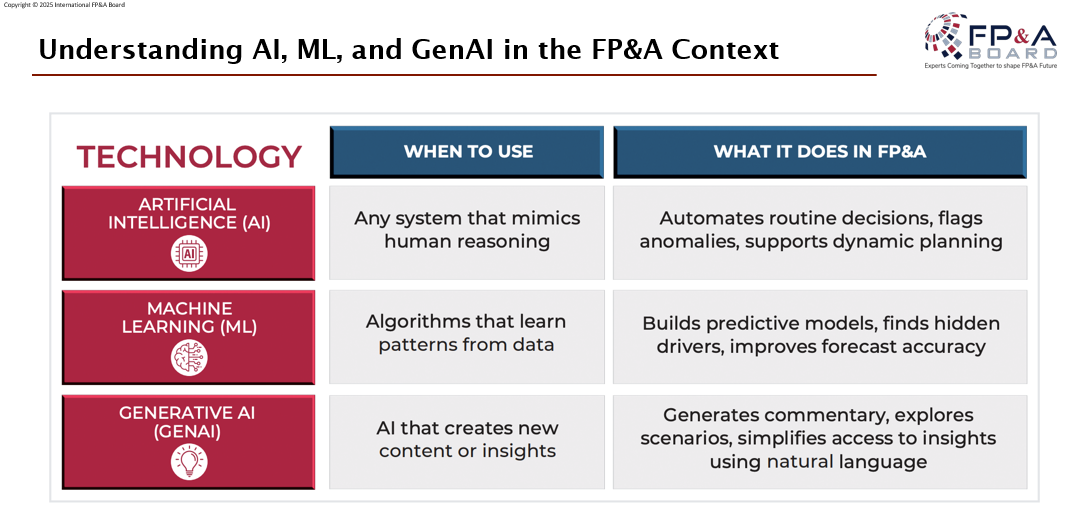
Figure 5
Case Studies: Industry Perspectives
Two short presentations enriched the session:
Gloria Zhang, Senior Director, FP&A at SunStrong Management, presented “The Role of FP&A in Organizational Transformation,” demonstrating how leadership and cross-functional collaboration drive cultural change in FP&A. The presentation focused on the question “Is it possible to budget the unpredictable?”
After a great discussion, one key quote that stood out was “FP&A is not just about managing budgets – it’s about guiding the company through uncertainty.”
Christine Maloney, Account Executive xP&A at SAP, demonstrated “How Modern Technology is Enabling Agentic AI in FP&A,” focusing on how AI enhances planning applications and agentic decision frameworks.
Group Work Outputs – Path to the Leading Stage
Participants collaborated in three breakout groups, each focused on a key pillar of the FP&A Trends Maturity Model: Systems and Processes, People and Culture, and Data and Models.
Group 1 – Systems and Processes
Group 1 emphasized the ongoing reliance on Excel, limited resources, and lack of time as major barriers to transformation. The group also highlighted the importance of data quality, metadata governance, and change management to ensure sustainable process improvement and technology adoption.

Group 2 – People and Culture
This group emphasized the importance of a clear FP&A vision that aligns with enterprise objectives. Strong influence and effective communication were seen as essential to achieving buy-in at all organizational levels. Participants described finance leaders as catalysts who drive transformation by connecting people, strategy, and technology.
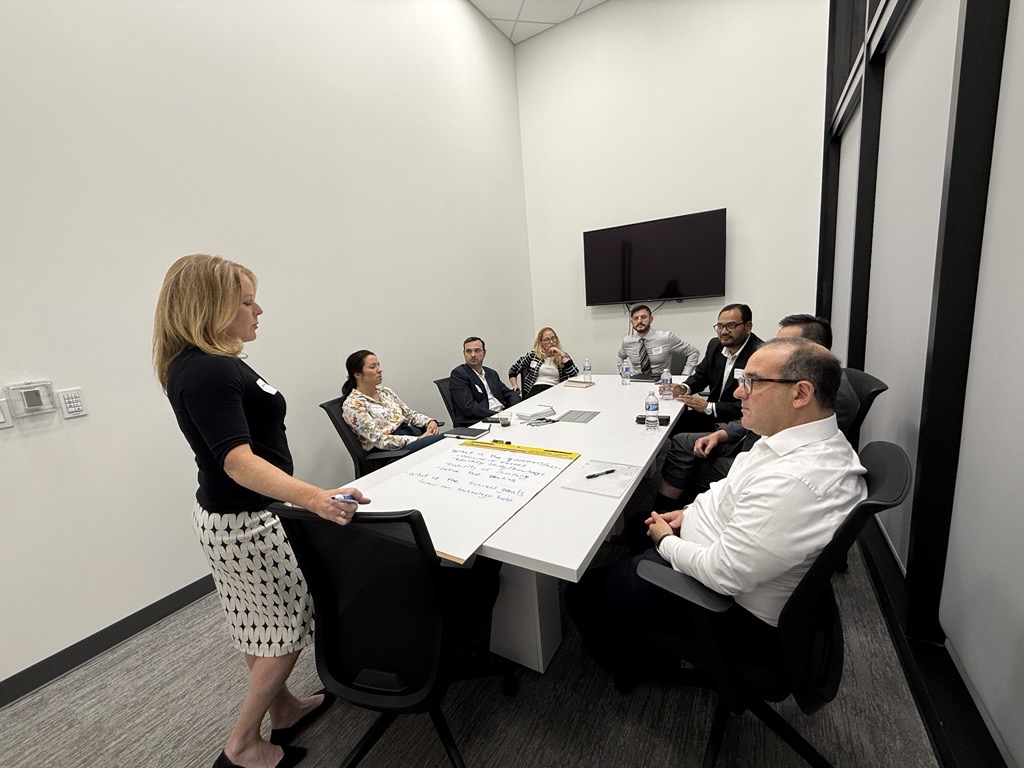

Group 3 – Data and Models
Group 3 underlined that data standardization and integrity form the foundation of FP&A maturity. They proposed creating a single master data structure and ensuring data security across systems. Their vision emphasized AI-human collaboration, where technology supports decision-making without replacing human judgment.

Conclusion
AI is not a silver bullet, but it is a powerful enabler of intelligent transformation. By embedding AI into FP&A processes, organizations can shift from reactive reporting to proactive, real-time decision-making. The future of FP&A is predictive, collaborative, and agile; those who invest now will be best positioned to thrive in uncertain times.









